Elon Musk Space Revolution Explained: SpaceX IPO, Starship, and the Multiplanetary Vision
Elon Musk Space Revolution Explained is the story of how a single entrepreneur transformed modern space exploration. Few individuals have reshaped the path of modern space exploration like Elon Musk, the founder and CEO of Space Exploration Technologies Corporation (SpaceX). Since its creation in 2002, SpaceX has transformed the aerospace industry from a slow-moving, government-dominated field into a thriving commercial frontier. Through an aggressive focus on reusable rocket technology, engineering efficiency, and cost reduction, Elon Musk’s Space Revolution and SpaceX have redefined the possibilities of orbital launch services.
Musk’s Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy rockets have become the benchmarks for reliability and reusability. Through lowering the cost of access to orbit for commercial, scientific, and government payloads, SpaceX’s rapid development cycles have made it the global leader in launch turnaround. These advancements have also significantly paved the way for the Starship program, a fully reusable super-heavy launch system designed for deep-space missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
Beyond just reusable rockets, Musk’s influence extends through additional programs such as Starlink, a global satellite constellation providing high-speed internet access worldwide. Together, these programs illustrate Musk’s revolutionary approach to spaceflight: making humanity a multiplanetary species capable of long-term survival beyond Earth.
As one of the most searched and discussed figures in technology and aerospace, Elon Musk continues to drive innovation at an unprecedented pace. Today, millions of space enthusiasts follow every Space Revolution milestone, from simple Falcon 9 launches to Starship test flights. You can follow all upcoming and past missions directly on the SpaceX Launch Schedule website to stay informed on all the latest information.
This article provides Elon Musk Space Revolution Explained, tracing SpaceX’s rise from Falcon 1 to Starship, Starlink, and the multiplanetary future.
Early Life and Influences
Elon Musk was born in Pretoria, South Africa, in 1971. From an early age, Musk showed a curiosity and fascination with technology and engineering. Further developing this early passion for computers, he taught himself to code and sold his first video game, Blastar, at age 12.
After moving to North America to pursue greater opportunities in technology, Musk earned degrees in physics and economics from the University of Pennsylvania.
Before founding SpaceX, Musk co-founded several successful startups, positioning him at the forefront of the digital revolution. His first significant endeavor, Zip2, provided online business directories and mapping software for newspapers, and was eventually sold for nearly $300 million. He then founded X.com, an online financial services company that later merged into PayPal. When PayPal was acquired by eBay in 2002, Musk’s earnings from the sale provided not only the capital but also the confidence to pursue a far more ambitious goal: revolutionizing access to space.
The Founding of SpaceX: The Beginning of Elon Musk’s Space Revolution
In 2002, Elon Musk founded Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) with the ambitious mission to reduce the cost of spaceflight, increase launch reliability, and ultimately enable human life on Mars. At the time, the global space industry was dominated by government agencies, where launches often cost hundreds of millions of dollars and rockets were used only once. Musk’s vision was revolutionary: he believed that through innovation and reusable rocket technology, access to space could become both affordable and sustainable.
The early years of SpaceX’s history were marked by intense challenges. The company’s first rocket, the Falcon 1, suffered three unsuccessful launch attempts between 2006 and 2008. Despite this pressure, Musk persevered. On September 28, 2008, the fourth Falcon 1 mission successfully reached orbit, making SpaceX the first private company in history to launch a liquid-fueled rocket into Earth orbit. This success immediately attracted attention from NASA, which soon awarded SpaceX a Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract, a turning point that ensured the company’s survival.
The Falcon Program: Breaking Barriers
The Falcon rocket program underpins SpaceX’s success. Named after the Millennium Falcon from Star Wars, the Falcon family exemplifies SpaceX’s engineering philosophy—rapid iteration and reusability.
Falcon 1 — The Proof of Concept
Falcon 1 was a two-stage, liquid-fueled vehicle designed to carry small payloads to low Earth orbit. Its success on September 28, 2008, demonstrated that a private company could achieve what had previously been reserved for national space agencies.
Falcon 9 — The Workhorse of Spaceflight
Introduced in June 2010, the Falcon 9 became the cornerstone of modern commercial spaceflight.
- Power: Nine Merlin engines in an “Octaweb” configuration.
- Reusability: Block 5 boosters are designed for up to 15+ reuses, with some now having flown 20+ missions.
- Record: It is currently the most launched rocket in the world, with over 350 successful flights.
For more information, visit the Falcon 9 Rocket Page.
Falcon Heavy — Power, Scale, and Spectacle
The Falcon Heavy features three Falcon 9 cores and 27 Merlin engines. Its maiden flight in 2018 captured global attention when it launched a Tesla Roadster into orbit. It remains the world’s most cost-effective heavy-lift vehicle, bridging the gap between Falcon 9 and the upcoming Starship system.
Starship — Musk’s Boldest Vision Yet
The Starship program is aimed at creating a fully reusable, super-heavy launch system capable of carrying humans and cargo to the Moon, Mars, and beyond. Standing nearly 120 meters tall, it is the largest and most powerful rocket ever built.
Design and Architecture
- Super Heavy Booster: The first stage powered by 33 Raptor engines.
- Starship Upper Stage: A spacecraft designed for long-duration crew or cargo transport.
Development and testing take place at Starbase in Boca Chica, Texas. Between 2023 and 2025, flights have shown rapid progress, including successful stage separation and controlled splashdowns. Starship is engineered to support NASA’s Artemis III and IV missions and future Mars colonization. Visit the Starship Rocket Launch Page for real-time updates.
Starlink — Future Among the Stars
Starlink is SpaceX’s global satellite internet constellation. With thousands of satellites in low Earth orbit (LEO), it is the largest satellite network ever created. Financially, Starlink is critical; the subscription model provides steady cash flow to fund the development of the Starship launch system and Mars mission planning.
How Elon Musk’s Space Revolution Changed the Global Space Industry
Musk’s influence has:
- Accelerated commercial spaceflight competition.
- Shifted NASA partnerships to fast-moving private companies.
- Pushed the entire industry toward reusability and lower launch costs.
By proving that reusable rockets can operate at scale, SpaceX has democratized access to space and inspired a new generation of entrepreneurs.
Elon Musk’s Vision for the Future : Space Revolution Explained
Musk’s long-term goal is to create a self-sustaining city on Mars. Beyond Mars, he sees space as a new industrial frontier, with a roadmap including lunar missions under the Artemis Program and interplanetary logistics systems. As Musk often explains, “If the future doesn’t include being out there among the stars, what’s the point of all this?”
Frequently Asked Questions: SpaceX & Elon Musk in 2026
Is SpaceX going public in 2026?
As of early 2026, reports indicate that SpaceX is actively preparing for a landmark Initial Public Offering (IPO). With valuations projected as high as $1.5 trillion, it is poised to be one of the most significant public debuts in history, driven largely by the recurring revenue from the Starlink constellation.
How many Starlink satellites are in orbit right now?
By January 2026, SpaceX has launched over 9,000 satellites. To improve space safety and reduce collision risks, the company recently began a major reconfiguration to lower the altitude of approximately 4,400 satellites from 550km to 480km.
When is the next Starship flight test?
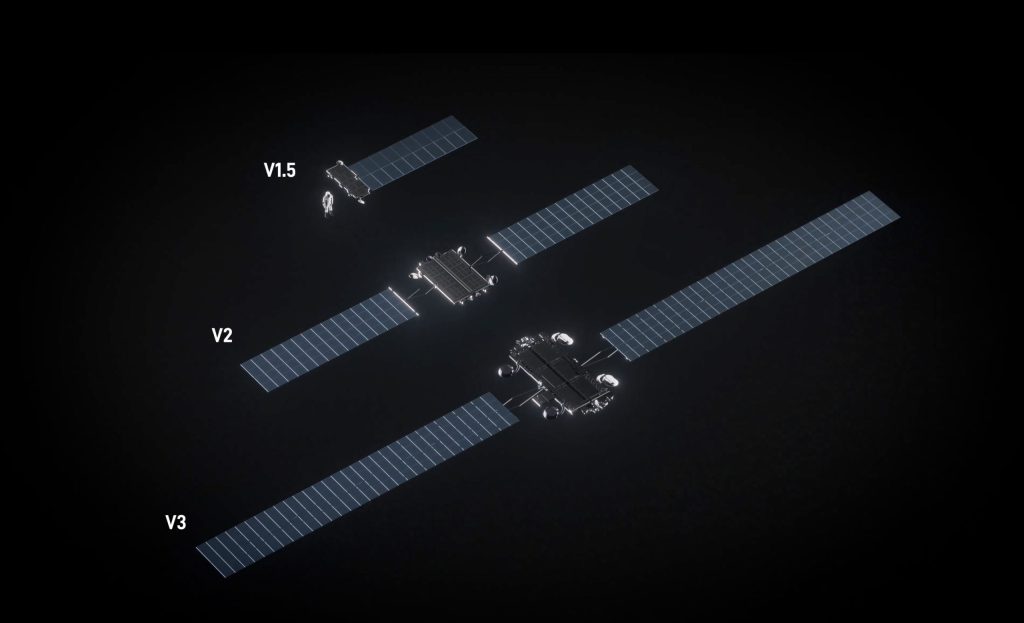
Starship Flight 12 is currently targeted for the first quarter of 2026. This mission is highly anticipated as it will feature the debut of the Version 3 (V3) hardware, designed for better orbital performance and preliminary tests of in-space propellant transfer.
When does NASA’s Artemis II mission launch?
NASA is currently targeting a launch window opening as early as February 5, 2026. Artemis II will be the first crewed mission to orbit the Moon since the Apollo era, carrying four astronauts on a 10-day journey aboard the Orion spacecraft.
What is Elon Musk’s space revolution?
Elon Musk Space Revolution Explained refers to SpaceX’s transformation of the aerospace industry through reusable rockets, rapid development cycles, Starship, and the goal of making humanity a multiplanetary species.
Conclusion
From a child fascinated with computers to the founder of the world’s most ambitious space company, Elon Musk has redefined the global space industry. Today, SpaceX continues to push the boundaries of possibility. For space enthusiasts, tracking every milestone is essential. Follow the Space Launch Schedule for upcoming missions and stay informed about the next steps in Elon Musk’s Space Revolution.