Pléiades-HR 1A, FASat-Charlie (SSOT), 4 x ELISA
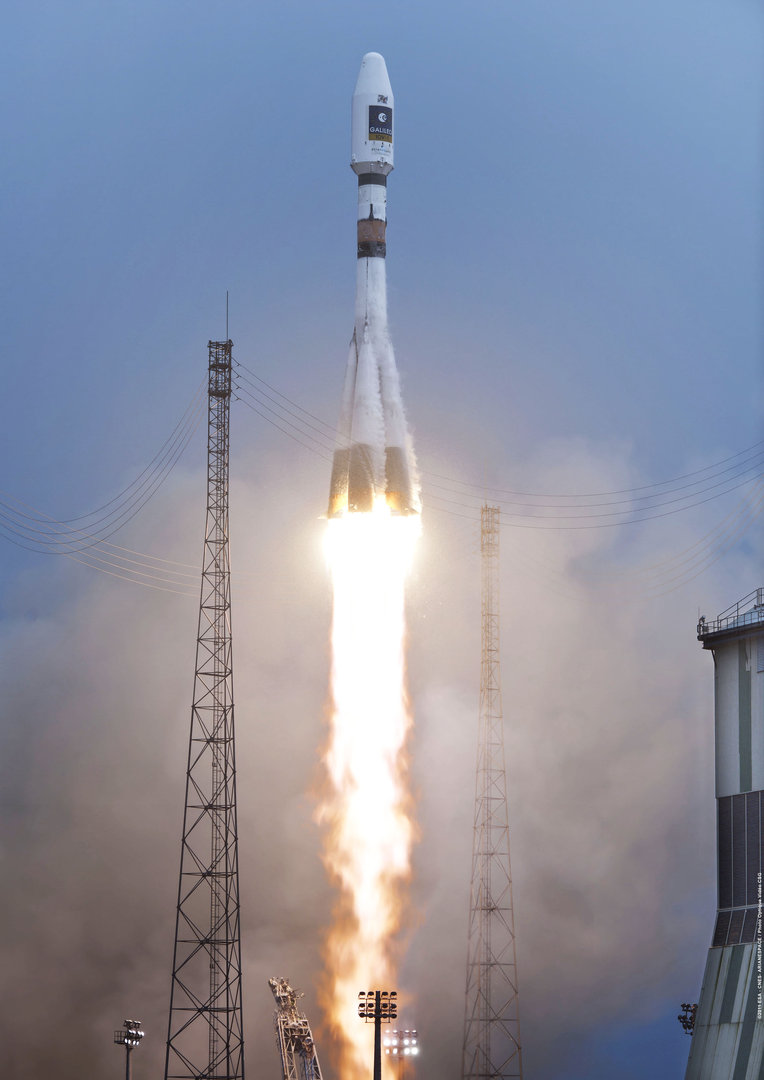
Soyuz STA/Fregat
Arianespace
Rocket Launch Video
Dailymotion: DailymotionRocket Launch Timeline
Enhance your rocket launch experience with a detailed timeline! From pre-launch preparations to post-launch milestones, a well-structured schedule ensures every step—payload prep, safety checks, and liftoff—runs smoothly. Stay informed and follow the action with precision.
| T- 04 : 20 : 00 | GO for Prop Load Launch director verifies go for propellant load |
| T- 04 : 00 : 00 | Prop Load Start of propelland loading |
| T- 01 : 45 : 00 | Prop Load Complete End of propellant loading |
| T- 01 : 00 : 00 | Mobile Gantry Rollback Rollback of the mobile gantry from the launch pad |
| T- 00 : 06 : 10 | Startup The onboard computer takes control over the countdown and runs last checks |
| T- 00 : 05 : 00 | Fregat Internal Power Fregat transitions to internal power |
| T- 00 : 02 : 25 | Umbilicals Separation Separation of umbilical connections |
| T- 00 : 00 : 40 | Internal Power Launch vehicle switches to internal power sources |
| T- 00 : 00 : 20 | Strongback Retract Retraction of the strongback arm ahead of liftoff |
| T- 00 : 00 : 17 | Ignition Start of the engine ignition sequence |
| T- 00 : 00 : 15 | Preliminary Thrust Preliminary thrust level achieved by the launch vehicle |
| T- 00 : 00 : 03 | Full Thrust Full thrust level achieved by the launch vehicle |
| T+ 00 : 00 : 00 | Liftoff First upwards movement of the rocket |
| T+ 00 : 01 : 58 | Boosters Separation Separation of the side boosters |
| T+ 00 : 03 : 29 | Fairing Separation Separation of the payload fairing |
| T+ 00 : 04 : 47 | Stage 2 Separation Separation of the second stage from the first |
| T+ 00 : 08 : 47 | Kick Stage Separation Separation of the kick stage from the previous stage |
| T+ 00 : 09 : 47 | Kick Stage Ignition Start of the kick stage engine |
| T+ 00 : 13 : 27 | Kick Stage Cut-off Cut-off of the kick stage engine |
| T+ 00 : 41 : 56 | Kick Stage Ignition Start of the kick stage engine |
| T+ 00 : 46 : 05 | Kick Stage Cut-off Cut-off of the kick stage engine |
| T+ 00 : 55 : 00 | Payload Separation Final deployment of the payload from the rocket |
| T+ 00 : 59 : 05 | Payload Separation Final deployment of the payload from the rocket |
| T+ 02 : 03 : 25 | Kick Stage Ignition Start of the kick stage engine |
| T+ 02 : 03 : 37 | Kick Stage Cut-off Cut-off of the kick stage engine |
| T+ 03 : 08 : 37 | Kick Stage Ignition Start of the kick stage engine |
| T+ 03 : 08 : 47 | Kick Stage Cut-off Cut-off of the kick stage engine |
| T+ 03 : 12 : 07 | Payload Separation Final deployment of the payload from the rocket |
| T+ 03 : 26 : 00 | Payload Separation Final deployment of the payload from the rocket |
Mission
Pléiades-HR 1A, FASat-Charlie (SSOT), 4 x ELISA
- Type: Government/Top Secret
- Orbit: Sun-Synchronous Orbit
Pléiades-HR 1A is the first of two high resolution Earth observation satellites designed by the French space agency (CNES) and manufactured by Astrium Satellites. The ELISA mission consists of four satellites manufactured by Astrium Satellites and Thales Systèmes Aéoroportés for the French space agency (CNES) and the French Directorate General of Armament (DGA). SSOT is an Earth observation satellite manufactured by Astrium Satellites for the Chilian armed forces.
Location
Soyuz Launch Complex
Guiana Space Centre, French Guiana
Soyuz Launch Complex has witnessed the launch of 26 rockets, including 26 orbital launch attempts. While Guiana Space Centre, French Guiana, has been the site for 331 rocket launches.
The Guiana Space Centre is a European spaceport to the northwest of Kourou in French Guiana, a region of France in South America. Kourou is located at a latitude of 5°. In operation since 1968, it is a suitable location for a spaceport because of its equatorial location and open sea to the east.
Rocket
Progress Rocket Space Center Soyuz STA Fregat
The 2.1a version includes conversion from analog to digital flight control system and uprated engines on the booster and the first stage with improved injection systems. The new digital flight control and telemetry systems allow the rocket to launch from a fixed rather than angled launch platform and adjust its heading in flight. A digital control system also enables the launch of larger commercial satellites with wider and longer payload fairings such as the ST-type fairing. These fairings introduce too much aerodynamic instability for the old analog system to handle. This stage continues to use the RD-0110 engine.
The 2.1a/ST version is sometimes called Soyuz ST-A.
Agency
Arianespace
Arianespace SA is a multinational company founded in 1980 as the world's first commercial launch service provider. It undertakes the production, operation, and marketing of the Ariane programme. Their vehicles launch exclusively from French Guiana in South America.