Inmarsat-6 F2
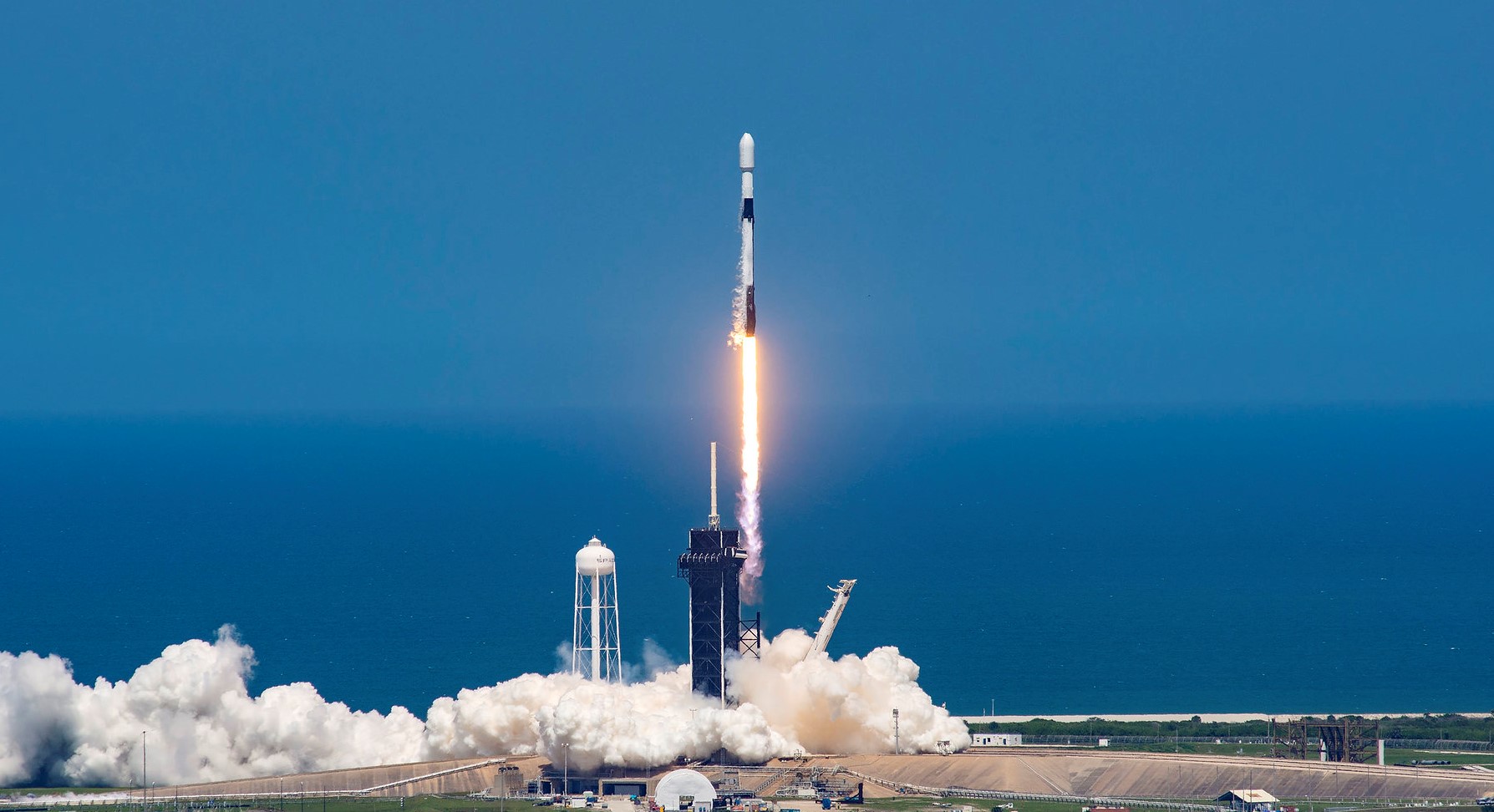
Falcon 9 Block 5
SpaceX
Weather Forecast During Launch
According to weather officials, there’s a 75% chance of favorable weather conditions at the time of the launch.
Trajectory
View comprehensive details including the rocket’s trajectory, velocity, altitude, thrust, and more at FlightClub.io.
Mission
Inmarsat-6 F2
- Type: Communications
- Orbit: Geostationary Transfer Orbit
- Launch Cost: $52,000,000
Inmarsat-6 is the sixth generation of satellites for the London-based global mobile satellite communications operator Inmarsat. It consists of a dual mission to augment both L-band and Ka-band Global Xpress services.
Airbus Defence and Space has been awarded a contract by Inmarsat to design and develop the first two Inmarsat-6 (I-6) mobile communications satellites, creating the most versatile mobile services satellites in its fleet.
The two I-6 satellites are based on Airbus Defence and Space’s Eurostar platform in its E3000e variant, which exclusively uses electric propulsion for orbit raising. The satellites take advantage of the reduction in mass that this electric propulsion technology enables for a dual payload mission, with an exceptionally large next generation digitally processed payload.
I-6 F1 and F2 both carry a large 9 m aperture L-band antenna and nine multibeam Ka-band antennas, and feature a high level of flexibility and connectivity. A new generation modular digital processor provides full routing flexibility over up to 8000 channels and dynamic power allocation to over 200 spot beams in L-band. Ka-band spot beams are steerable over the full Earth disk, with flexible channel to beam allocation.
Location
Rocket
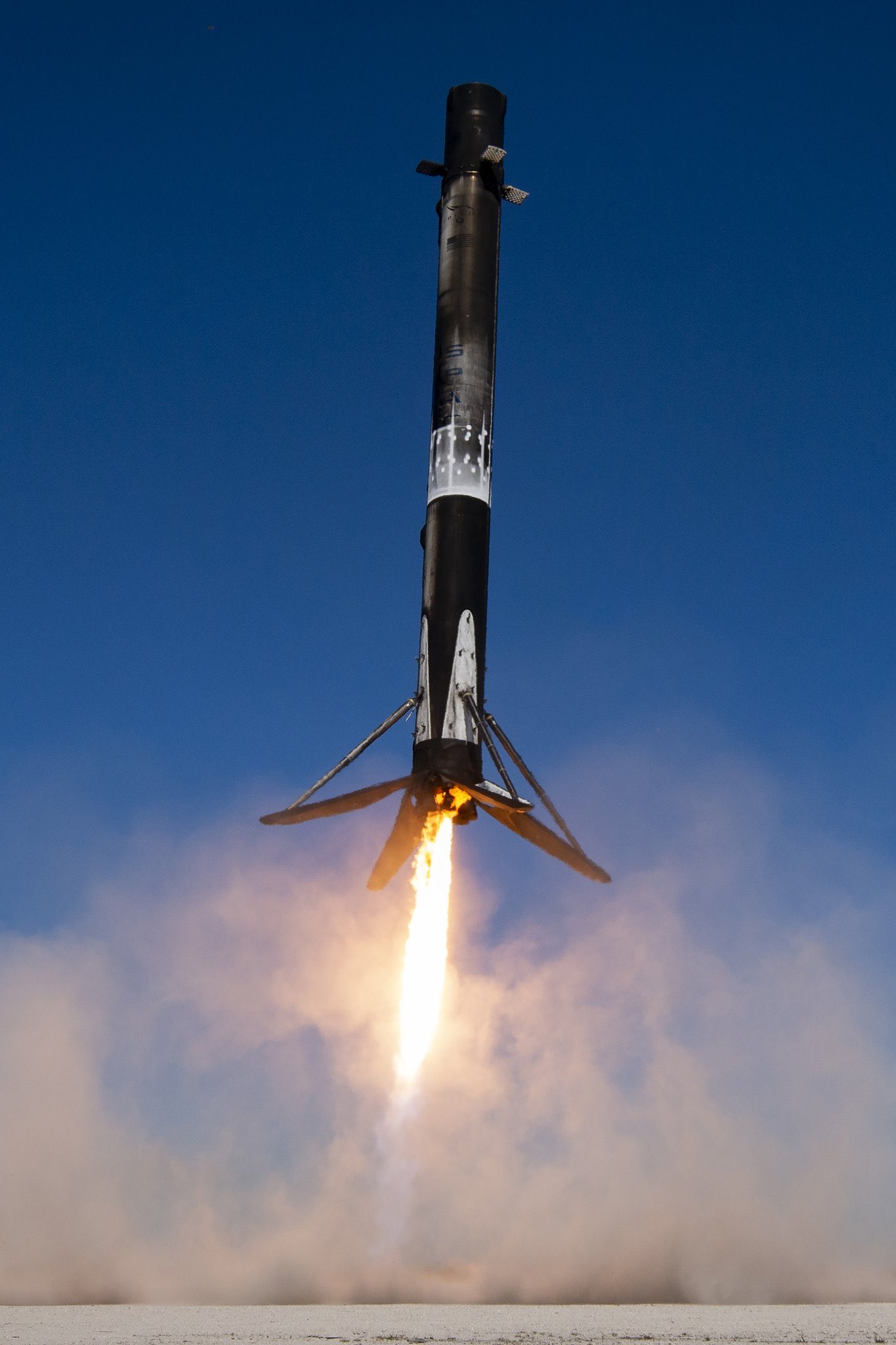
Landing
Core B1077
Booster B1077 last launched 03/10/2024 and has seen 11 successful launches and landings. Falcon 9 Block 5 booster first used for the Crew-5 mission.
Just Read the Instructions – JRTI
Third (Marmac 303) ASDS barge, Just Read the Instructions (JRTI) is currently used to recover Falcon 9 and Heavy boosters in the Altantic Ocean.
Autonomous Spaceport Drone Ship – ASDS
An autonomous spaceport drone ship (ASDS) is an ocean-going vessel derived from a deck barge, outfitted with station-keeping engines and a large landing platform. Construction of such ships was commissioned by aerospace company SpaceX to allow for recovery of rocket first-stages at sea for high-velocity missions which do not carry enough fuel to return to the launch site after lofting spacecraft onto an orbital trajectory.
Agency
SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp., known as SpaceX, is an American aerospace manufacturer and space transport services company headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by entrepreneur Elon Musk with the goal of reducing space transportation costs and enabling the colonization of Mars. SpaceX operates from many pads, on the East Coast of the US they operate from SLC-40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station and historic LC-39A at Kennedy Space Center. They also operate from SLC-4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California, usually for polar launches. Another launch site is being developed at Boca Chica, Texas.