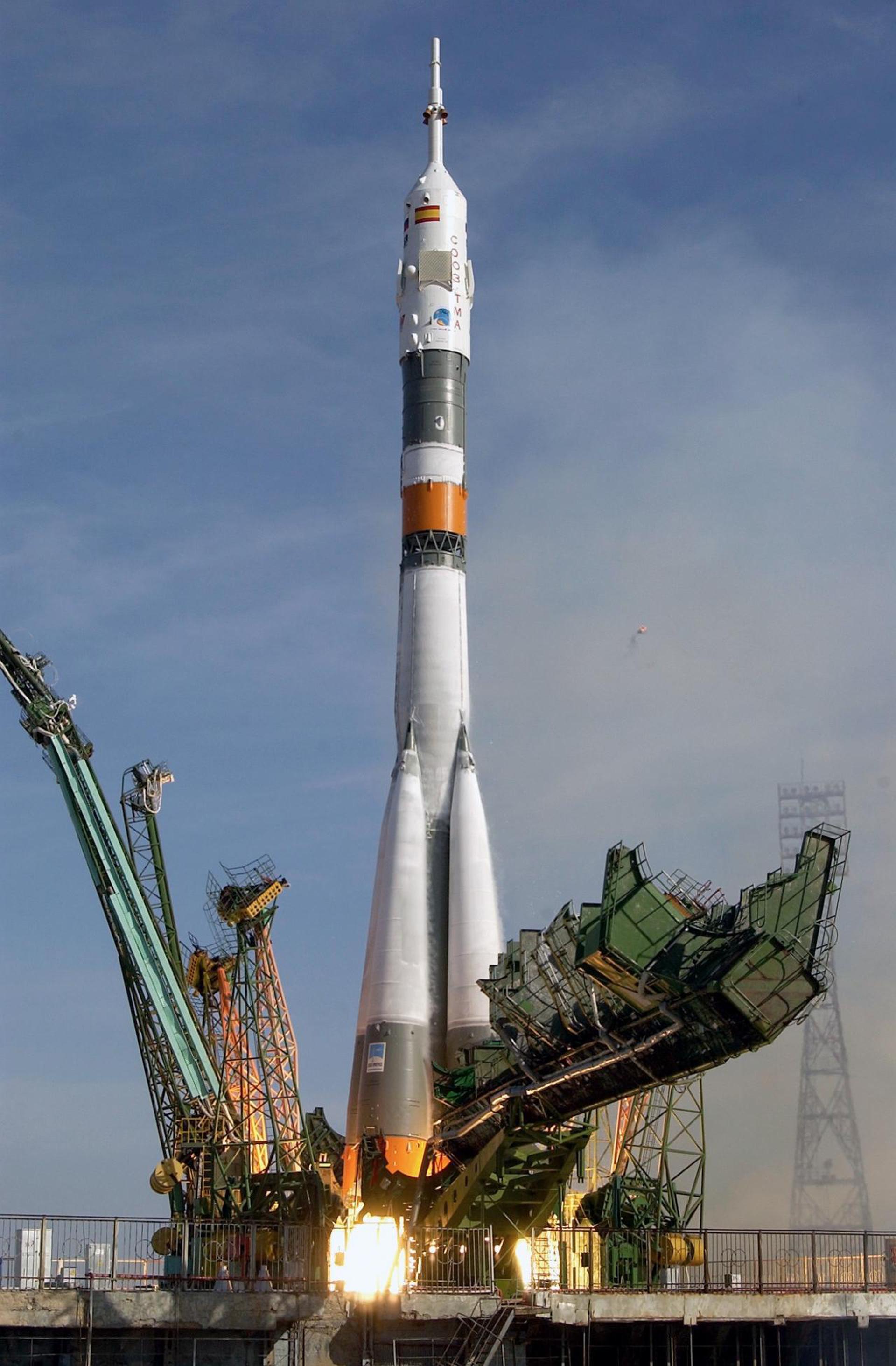
Soyuz 39
Soyuz-U
Soviet Space Program
Crew

Vladimir Dzhanibekov
- Birthday: 05/13/1942
- Role: Commander
- Nationality: Russian
- First Flight: 01/10/1978
- Last Flight: 06/06/1985
Vladimir Aleksandrovich Dzhanibekov (Russian: Владимир Александрович Джанибеков, born 13 May 1942) is a former cosmonaut who made five flights.
Dzhanibekov made five flights: Soyuz 27, Soyuz 39, Soyuz T-6, Soyuz T-12 and Soyuz T-13. In all he had spent 145 days, 15 hours and 56 minutes in space over these five missions. He had also performed two EVAs with a total time of 8 hours and 35 minutes. In 1985 he noted the effects of the tennis racket theorem, subsequently also called the Dzhanibekov effect, by showing that an object’s second principal axis is unstable while in free-fall rotation.

Jügderdemidiin Gürragchaa
- Birthday: 12/05/1947
- Role: Research Cosmonaut
- Nationality: Mongolian
- First Flight: 03/22/1981
- Last Flight: 03/22/1981
Jügderdemidiin Gürragchaa, born 5 December 1947) was the first Mongolian in space.
He was selected as part of the eighth Intercosmos program on 1 March 1978, at time he was in the rank of Major General. His backup was Maidarjavyn Ganzorig. Gürragchaa, along with Soviet cosmonaut Vladimir Dzhanibekov, departed from Baikonur Cosmodrome on 22 March 1981. They docked with Salyut 6.
While in orbit, Dzhanibekov and Gürragchaa carried out experiments on earth science. After 124 orbits and 7 days, 20 hours and 42 minutes in space, Gürragchaa and Dzhanibekov landed 170 km southeast of Dzhezkasgan.
Mission
Soyuz 39
- Type: Human Exploration
- Orbit: Low Earth Orbit
Soyuz 39 was the 15th mission to visit the Salyut 6 space station and carried the the EP-9 crew, which visited the long-duration Soyuz T-4 resident crew. The mission began on March 22, 1981, 14:58, launching Commander Vladimir Dzhanibekov and Research Cosmonaut Jügderdemidiin Gürragchaa, the first Mongolian cosmonaut, into orbit. They docked with the station the next day. During their 7-day stay on the station, EP-9 crew conducted Earth observation, material, medical and other experiments, including cosmic radiation research.
The mission concluded with a safe landing back on Earth on March 30, 1981, 11:40:58 UTC.
Location
1/5
Baikonur Cosmodrome, Republic of Kazakhstan
1/5 has witnessed the launch of 487 rockets, including 487 orbital launch attempts, while Baikonur Cosmodrome, Republic of Kazakhstan, has been the site for 1547 rocket launches.
Rocket
Agency
Soviet Space Program
The Soviet space program, was the national space program of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) actived from 1930s until disintegration of the Soviet Union in 1991.
The Soviet Union’s space program was mainly based on the cosmonautic exploration of space and the development of the expandable launch vehicles, which had been split between many design bureaus competing against each other. Over its 60-years of history, the Russian program was responsible for a number of pioneering feats and accomplishments in the human space flight, including the first intercontinental ballistic missile (R-7), first satellite (Sputnik 1), first animal in Earth orbit (the dog Laika on Sputnik 2), first human in space and Earth orbit (cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin on Vostok 1), first woman in space and Earth orbit (cosmonaut Valentina Tereshkova on Vostok 6), first spacewalk (cosmonaut Alexei Leonov on Voskhod 2), first Moon impact (Luna 2), first image of the far side of the Moon (Luna 3) and unmanned lunar soft landing (Luna 9), first space rover (Lunokhod 1), first sample of lunar soil automatically extracted and brought to Earth (Luna 16), and first space station (Salyut 1). Further notable records included the first interplanetary probes: Venera 1 and Mars 1 to fly by Venus and Mars, respectively, Venera 3 and Mars 2 to impact the respective planet surface, and Venera 7 and Mars 3 to make soft landings on these planets.