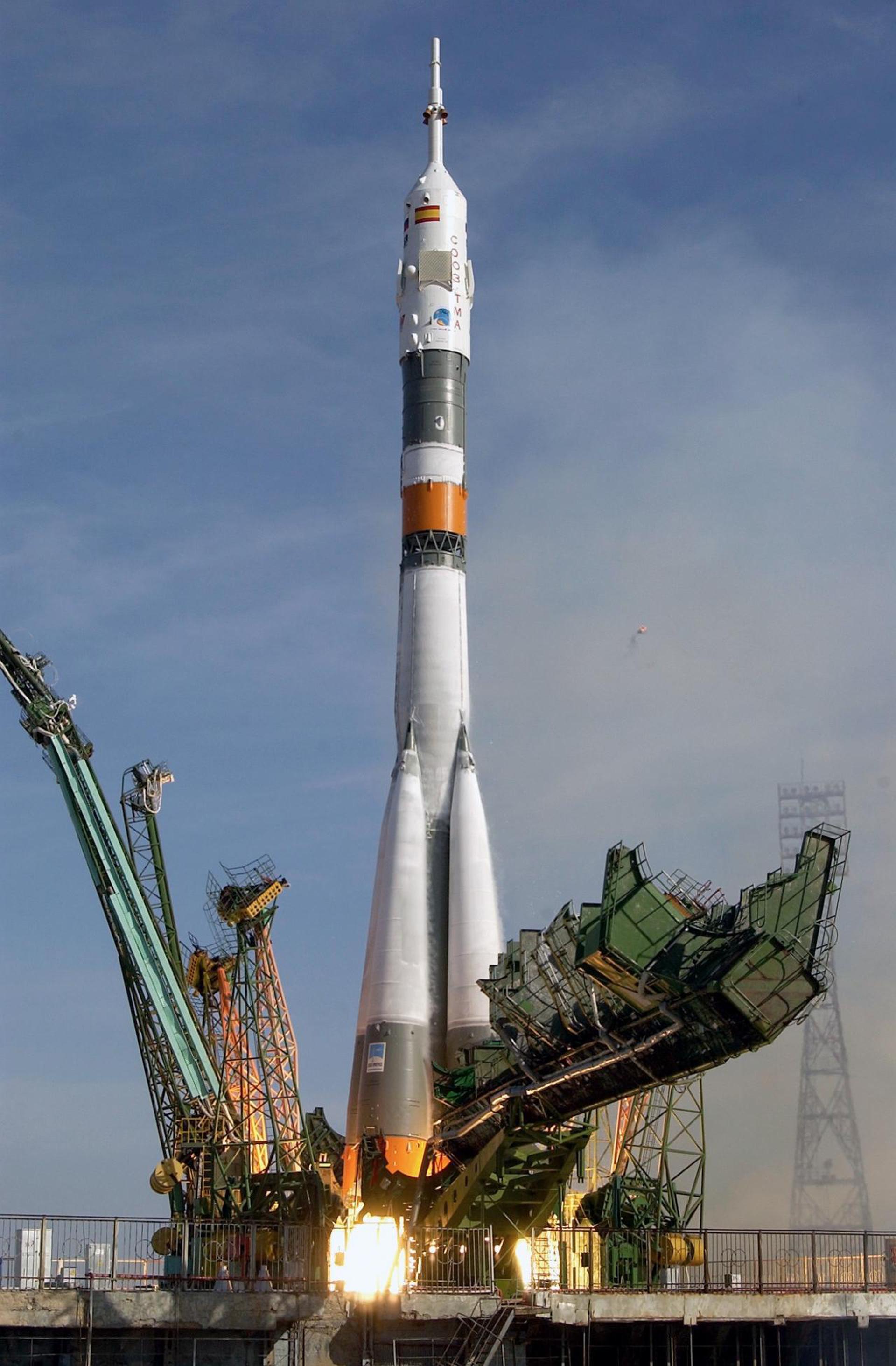
Soyuz 31
Soyuz-U
Soviet Space Program
Crew

Valery Bykovsky
- Birthday: 08/02/1934
- Role: Commander
- Nationality: Russian
- First Flight: 06/14/1963
- Last Flight: 08/26/1978
Valery Fyodorovich Bykovsky (Russian: Вале́рий Фёдорович Быко́вский; born 2 August 1934) is a retired Soviet cosmonaut who flew three manned space mission space flights: Vostok 5, Soyuz 22, and Soyuz 31. He was also backup for Vostok 3 and Soyuz 37.

Sigmund Jähn
- Birthday: 02/13/1937
- Role: Research Cosmonaut
- Nationality: German
- First Flight: 08/26/1978
- Last Flight: 08/26/1978
Sigmund Werner Paul Jähn (born 13 February 1937) is a German cosmonaut and pilot, who in 1978 became the first German to fly in space as part of the Soviet Union’s Interkosmos programme.
Mission
Soyuz 31
- Type: Human Exploration
- Orbit: Low Earth Orbit
Soyuz 31 was the sixth mission to visit the Salyut 6 space station and carried the the EP-4 crew, which visited the long-duration Soyuz 29 resident crew. The mission began on August 26, 1978, 14:51:30 UTC, launching Commander Valery Bukovsky and Research Cosmonaut/Flight Engineer Sigmund Jähn, the first German cosmonaut, into orbit. They docked with the station the next day. During their stay on the station, crew conducted various scientific experiments. Soyuz 31 crew swapped vehicles with the Soyuz 29 (EO-2 expedition) crew, which allowed for a longer stay in orbit for EO-2.
The mission concluded with a safe landing back on Earth on September 3, 1978, 11:40:34 UTC.
Location
Rocket
Agency
Soviet Space Program
The Soviet space program, was the national space program of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) actived from 1930s until disintegration of the Soviet Union in 1991.
The Soviet Union’s space program was mainly based on the cosmonautic exploration of space and the development of the expandable launch vehicles, which had been split between many design bureaus competing against each other. Over its 60-years of history, the Russian program was responsible for a number of pioneering feats and accomplishments in the human space flight, including the first intercontinental ballistic missile (R-7), first satellite (Sputnik 1), first animal in Earth orbit (the dog Laika on Sputnik 2), first human in space and Earth orbit (cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin on Vostok 1), first woman in space and Earth orbit (cosmonaut Valentina Tereshkova on Vostok 6), first spacewalk (cosmonaut Alexei Leonov on Voskhod 2), first Moon impact (Luna 2), first image of the far side of the Moon (Luna 3) and unmanned lunar soft landing (Luna 9), first space rover (Lunokhod 1), first sample of lunar soil automatically extracted and brought to Earth (Luna 16), and first space station (Salyut 1). Further notable records included the first interplanetary probes: Venera 1 and Mars 1 to fly by Venus and Mars, respectively, Venera 3 and Mars 2 to impact the respective planet surface, and Venera 7 and Mars 3 to make soft landings on these planets.