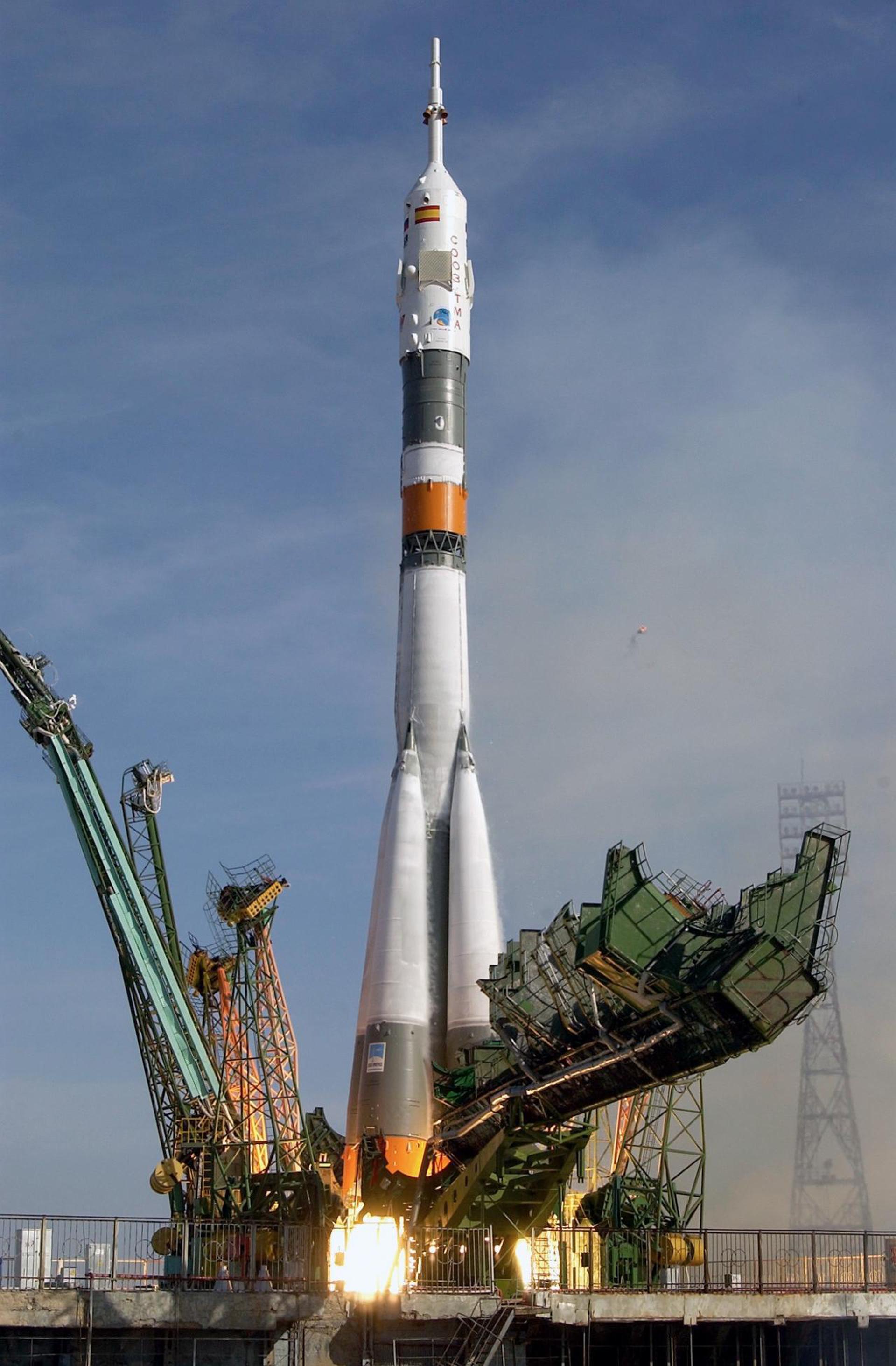
Soyuz 19
Soyuz-U
Soviet Space Program
Crew

Alexey Leonov
- Birthday: 05/30/1934
- Role: Commander
- Nationality: Russian
- First Flight: 03/18/1965
- Last Flight: 07/15/1975
Alexey Arkhipovich Leonov (Russian: Алексе́й Архи́пович Лео́нов, IPA: [ɐlʲɪˈksʲej ɐˈrxʲipəvʲɪtɕ lʲɪˈonəf]; born 30 May 1934) is a retired Soviet/Russian cosmonaut, Air Force Major general, writer and artist. On 18 March 1965, he became the first human to conduct extravehicular activity (EVA), exiting the capsule during the Voskhod 2 mission for a 12-minute spacewalk.

Valeri Kubasov
- Birthday: 01/07/1935
- Role: Flight Engineer
- Nationality: Russian
- First Flight: 10/11/1969
- Last Flight: 05/26/1980
Valeri Nikolayevich Kubasov (Russian: Вале́рий Никола́евич Куба́сов; 7 January 1935 – 19 February 2014) was a Soviet/Russian cosmonaut who flew on two missions in the Soyuz programme as a flight engineer: Soyuz 6 and Soyuz 19 (the Apollo–Soyuz mission), and commanded Soyuz 36 in the Intercosmos programme. On 21 July 1975, the Soyuz 7K-TM module used for ASTP landed in Kazakhstan at 5:51 p.m. and Kubasov was the first to exit the craft. Kubasov performed the first welding experiments in space, along with Georgy Shonin.
Mission
Soyuz 19
- Type: Human Exploration
- Orbit: Low Earth Orbit
Soyuz 19 was a part of the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project, which was the first joint US-Soviet space flight.
The Soviet side of mission began on July 15, 1975, 12:20:00 UTC, launching Commander Alexey Leonov and Flight Engineer Valeri Kubasov into orbit. Two days later, they docked with the Apollo spacecraft. American and Soviet crews visited each other’s spacecrafts, performed docking and redocking maneuvers, conducted joint scientific experiments, exchanged flags and gifts. Crews spent more than 44 hours together, and after final parting of the ships Soviet crew spent five more days in orbit.
Soyuz 19 returned to Earth with a safe landing on July 21, 1975, 10:50:00 UTC.
Location
Rocket
Agency
Soviet Space Program
The Soviet space program, was the national space program of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) actived from 1930s until disintegration of the Soviet Union in 1991.
The Soviet Union’s space program was mainly based on the cosmonautic exploration of space and the development of the expandable launch vehicles, which had been split between many design bureaus competing against each other. Over its 60-years of history, the Russian program was responsible for a number of pioneering feats and accomplishments in the human space flight, including the first intercontinental ballistic missile (R-7), first satellite (Sputnik 1), first animal in Earth orbit (the dog Laika on Sputnik 2), first human in space and Earth orbit (cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin on Vostok 1), first woman in space and Earth orbit (cosmonaut Valentina Tereshkova on Vostok 6), first spacewalk (cosmonaut Alexei Leonov on Voskhod 2), first Moon impact (Luna 2), first image of the far side of the Moon (Luna 3) and unmanned lunar soft landing (Luna 9), first space rover (Lunokhod 1), first sample of lunar soil automatically extracted and brought to Earth (Luna 16), and first space station (Salyut 1). Further notable records included the first interplanetary probes: Venera 1 and Mars 1 to fly by Venus and Mars, respectively, Venera 3 and Mars 2 to impact the respective planet surface, and Venera 7 and Mars 3 to make soft landings on these planets.