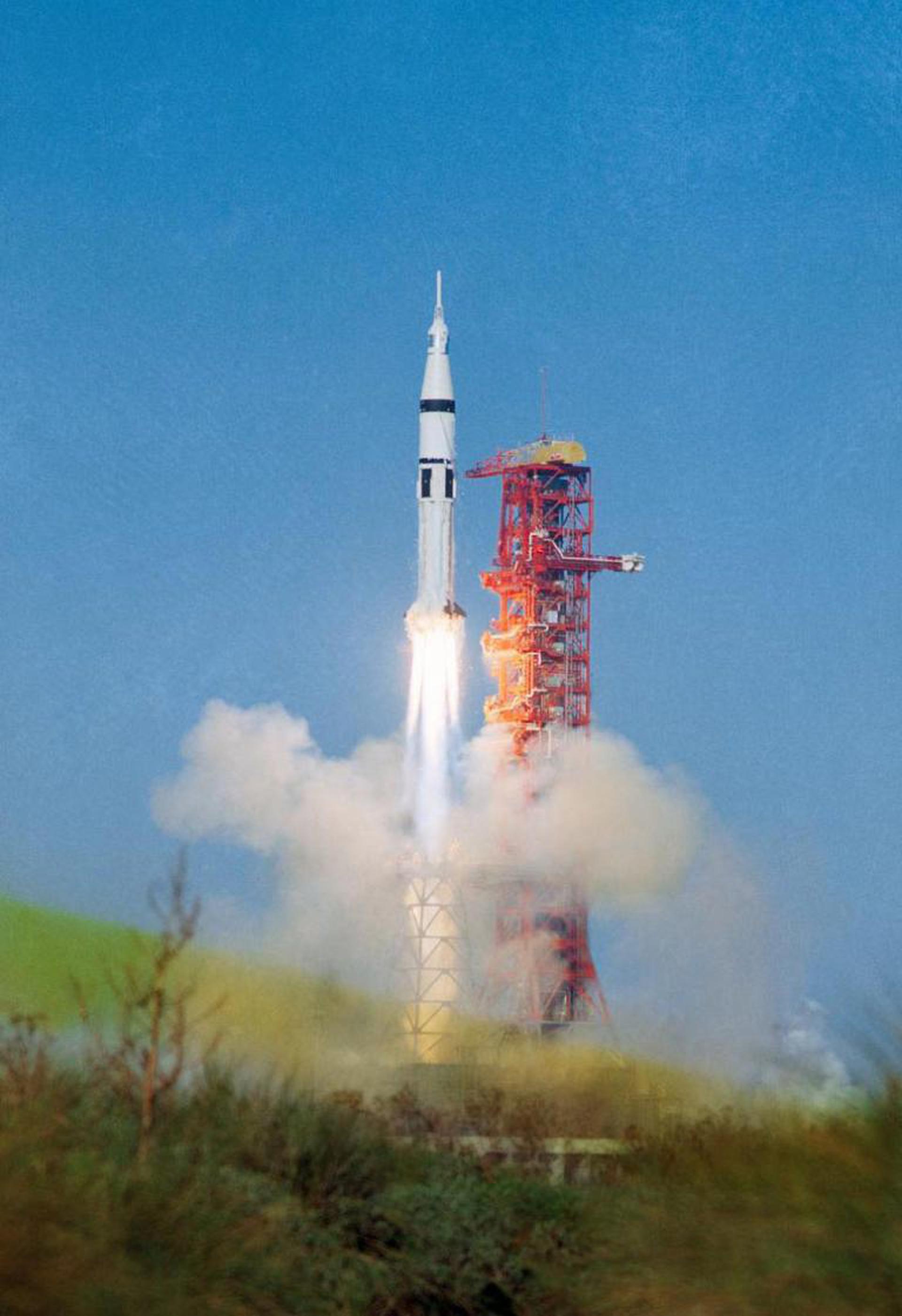
Skylab 2
Saturn IB
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
Crew
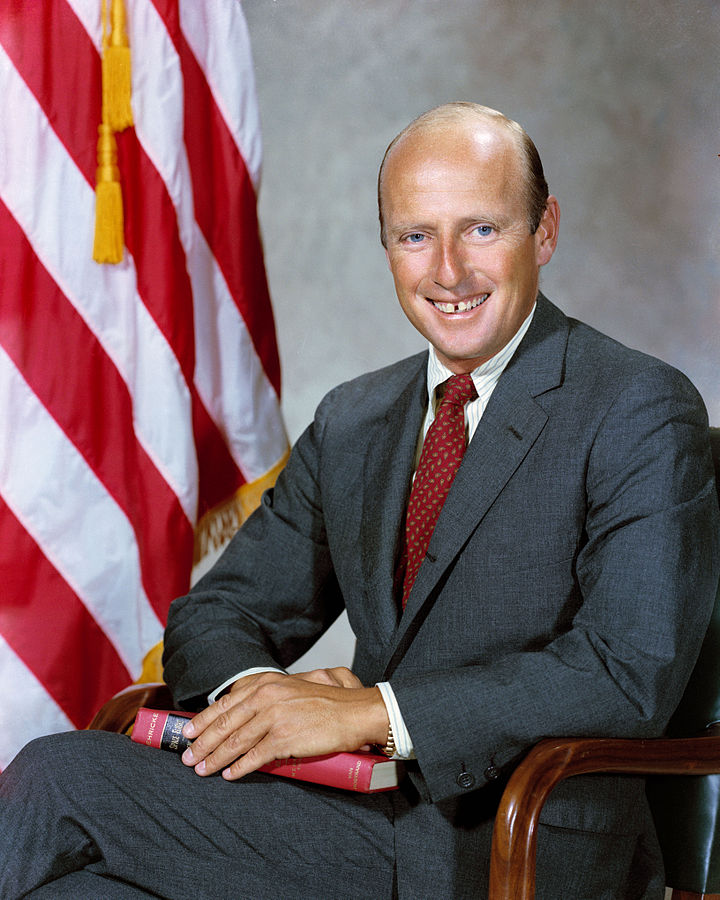

Pete Conrad
- Birthday: 06/02/1930
- Role: Commander
- Nationality: American
- First Flight: 08/21/1965
- Last Flight: 05/25/1973
Charles “Pete” Conrad Jr. was an American NASA astronaut, aeronautical engineer, naval officer and aviator, test pilot, and during the Apollo 12 mission became the third man to walk on the Moon. Conrad was selected in NASA’s second astronaut class.
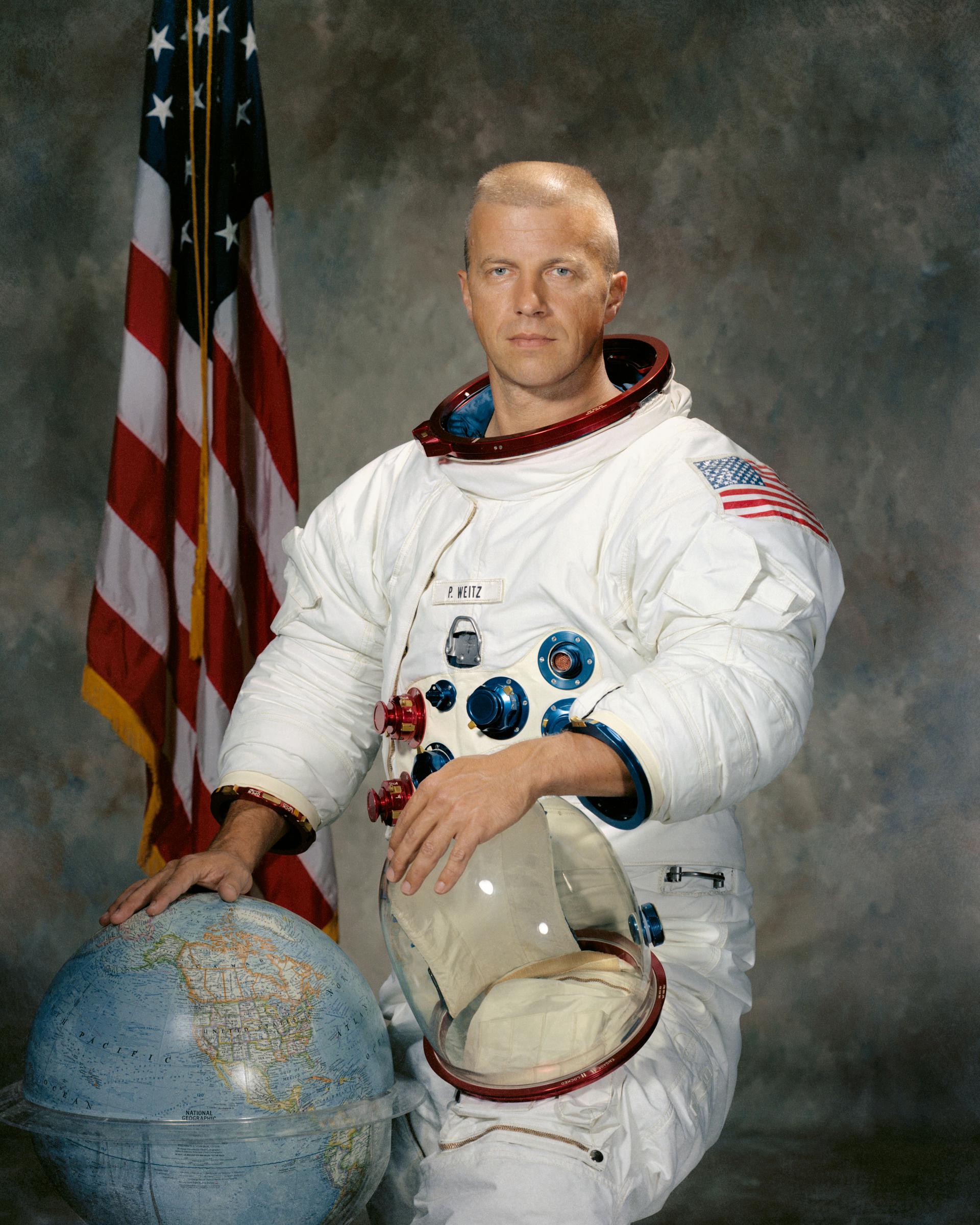

Paul J. Weitz
- Birthday: 07/25/1932
- Role: Pilot
- Nationality: American
- First Flight: 05/25/1973
- Last Flight: 04/04/1983
Paul Joseph Weitz was an American naval officer and aviator, aeronautical engineer, test pilot, and NASA astronaut, who flew into space twice. He was a member of the three-man crew who flew on Skylab 2, the first manned Skylab mission. He was also Commander of the STS-6 mission, the first of the Space Shuttle Challenger flights.
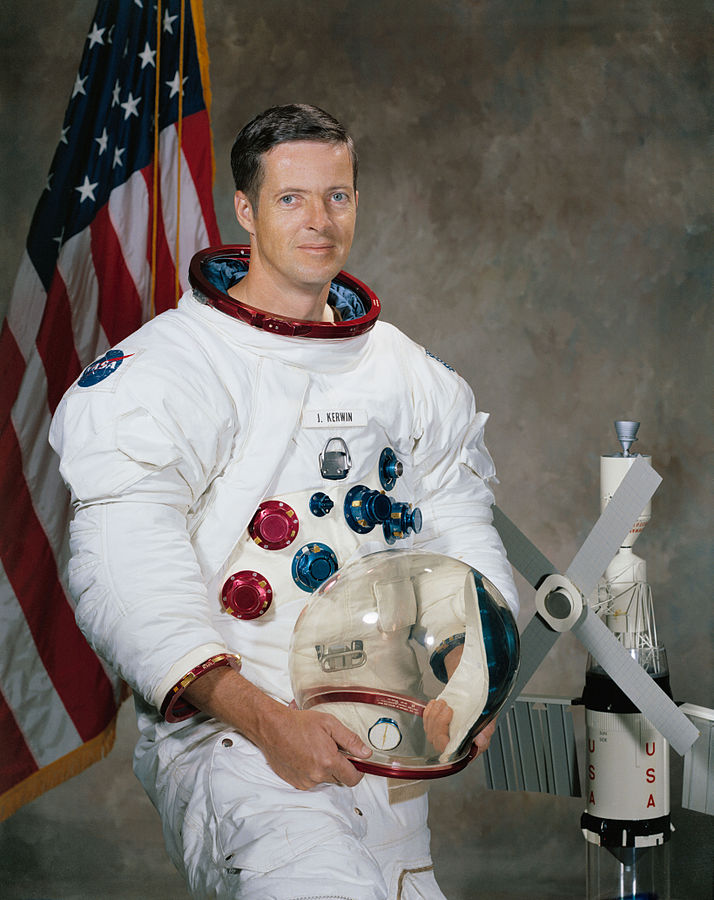

Joseph P. Kerwin
- Birthday: 02/19/1932
- Role: Science Pilot
- Nationality: American
- First Flight: 05/25/1973
- Last Flight: 05/25/1973
Joseph Peter Kerwin, M.D. is an American physician and former NASA astronaut, who served as Science Pilot for the Skylab 2 mission from May 25–June 22, 1973. He was the first physician to be selected for astronaut training.
Mission
Skylab 2
- Type: Human Exploration
- Orbit: Low Earth Orbit
Skylab 2 (also known as SL-2 or SLM-1) was the first crewed mission to the first US orbital space station Skylab. The mission began on May 25, 1973, 13:00:00 UTC with the launch of a three-person crew. Crew members were the Commander Charles “Pete” Conrad, Jr., Science Pilot Joseph P. Kerwin and Pilot Paul J. Weitz. During their 26-day stay on the station, crew performed station repairs and conducted scientific, medical experiments, gathered solar and Earth science data. The mission ended successfully with the splashdown in the Pacific Ocean on June 22, 1973, 13:49:48 UTC.
Location
Rocket
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Saturn IB
The Saturn IB (pronounced “one B”, also known as the Uprated Saturn I) was an American launch vehicle commissioned by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) for the Apollo program. It replaced the S-IV second stage of the Saturn I with the much more powerful S-IVB, able to launch a partially fueled Apollo Command/Service Module (CSM) or a fully fueled Lunar Module (LM) into low Earth orbit for early flight tests before the larger Saturn V needed for lunar flight was ready.
Agency
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for the civilian space program, as well as aeronautics and aerospace research. NASA have many launch facilities but most are inactive. The most commonly used pad will be LC-39B at Kennedy Space Center in Florida.