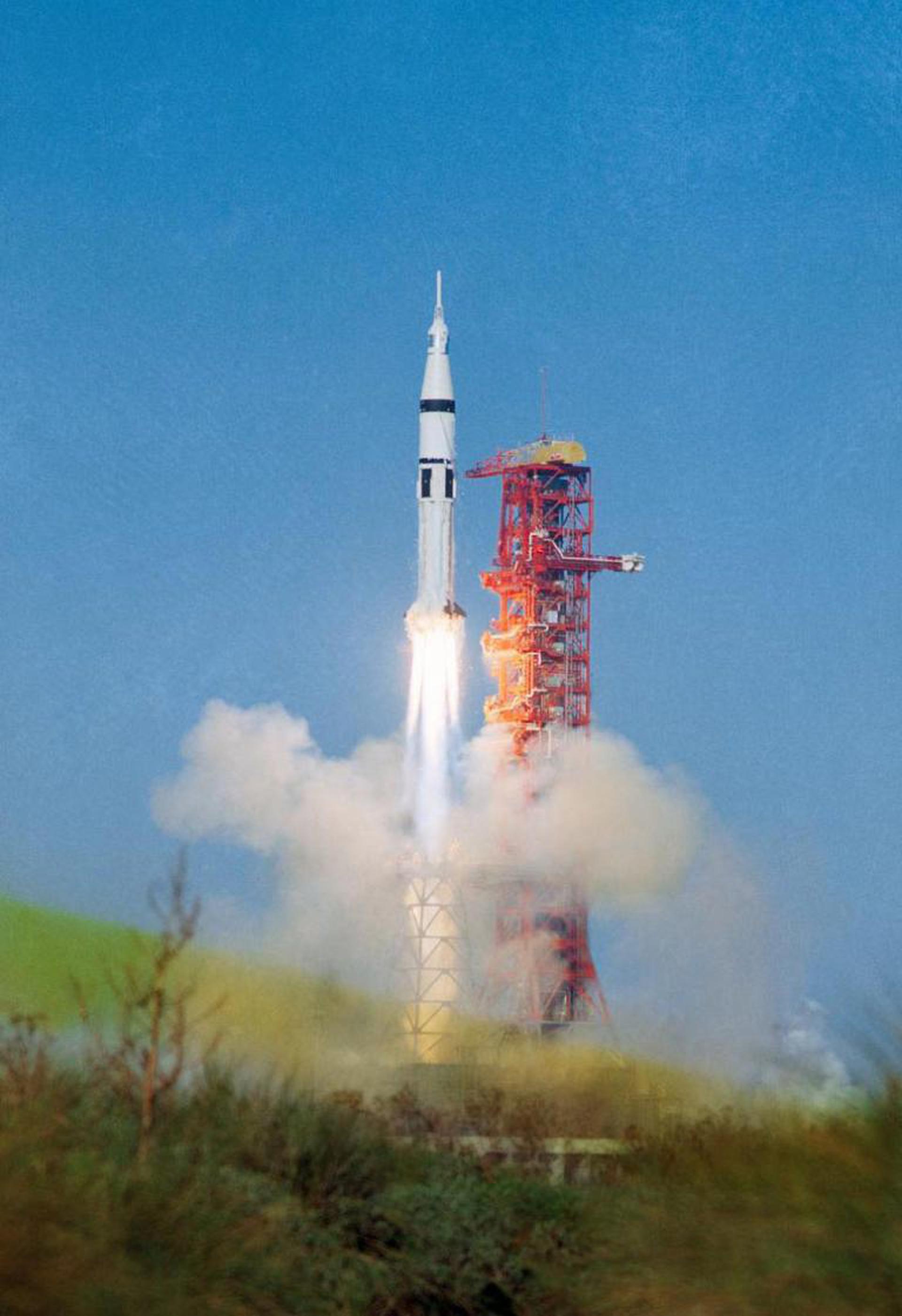
Apollo-Soyuz Test Project
Saturn IB
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
Crew
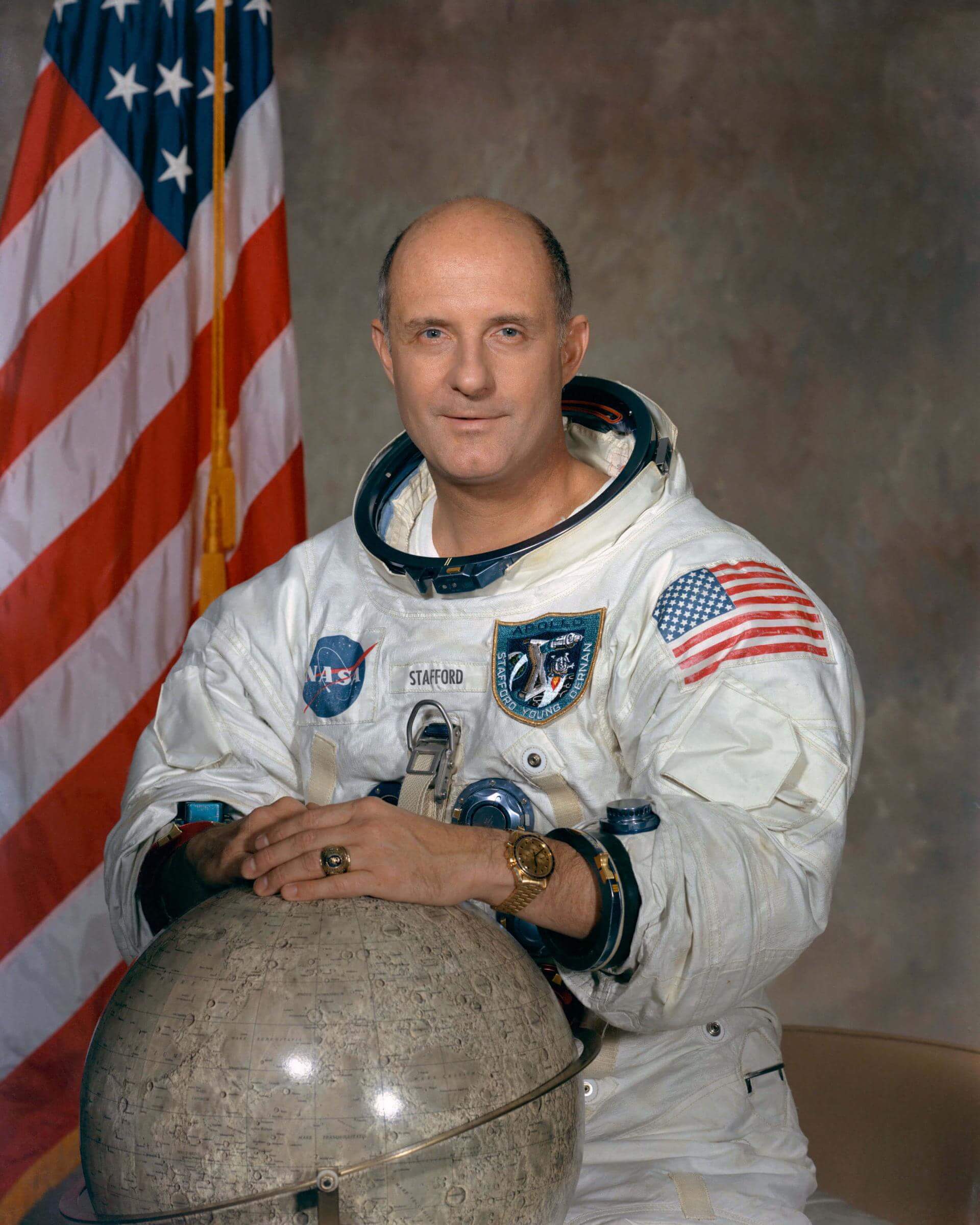

Thomas P. Stafford
- Birthday: 09/17/1930
- Role: Commander
- Nationality: American
- First Flight: 12/15/1965
- Last Flight: 07/15/1975
Thomas Patten Stafford was an American Air Force officer, test pilot, and NASA astronaut.
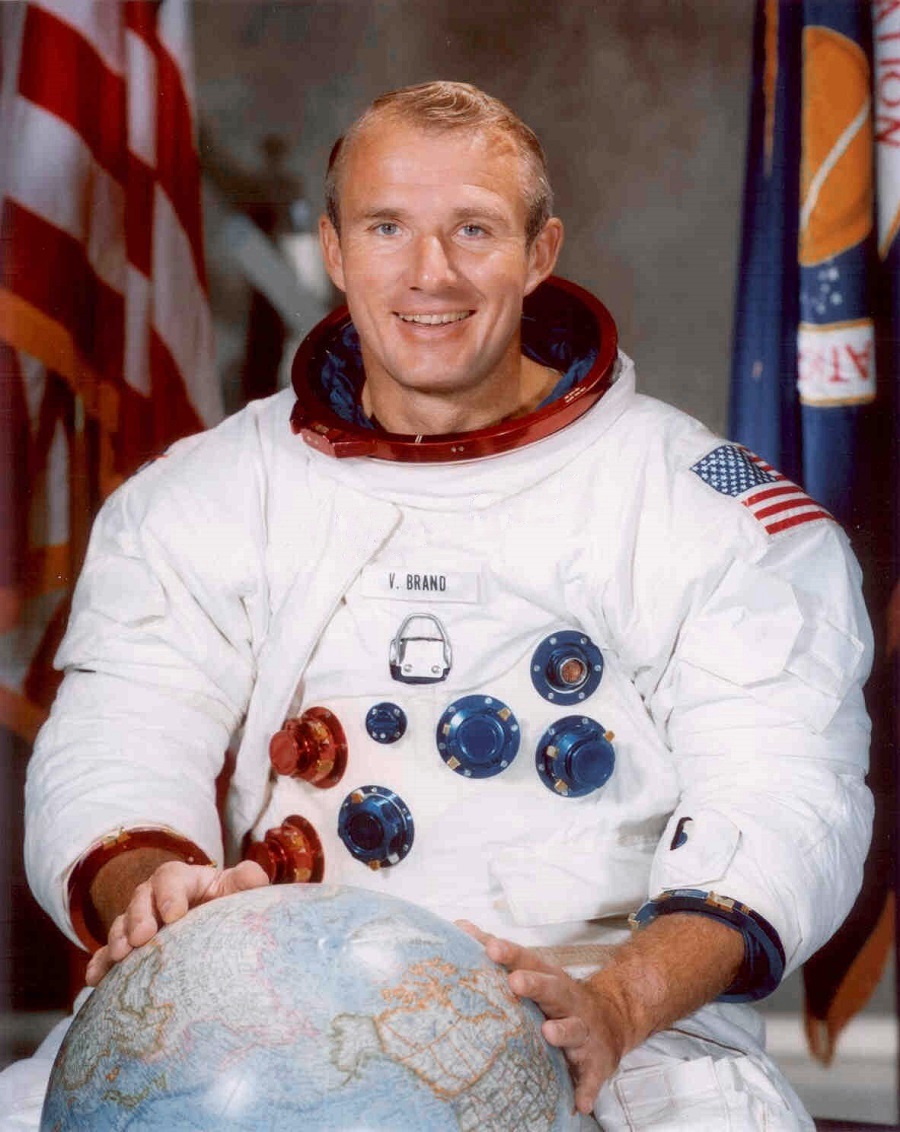

Vance D. Brand
- Birthday: 05/09/1931
- Role: Command Module Pilot
- Nationality: American
- First Flight: 07/15/1975
- Last Flight: 12/02/1990
Vance DeVoe Brand is an American former naval officer and aviator, aeronautical engineer, test pilot, and NASA astronaut. He served as Command Module Pilot during the first U.S.-Soviet joint spaceflight in 1975, and as Commander of three Space Shuttle missions.
His flight experience includes 9,669 flying hours, which includes 8,089 hours in jets, 391 hours in helicopters, 746 hours in spacecraft, and checkout in more than 30 types of military aircraft. Vance Brand Airport in Longmont, Colorado, is named in his honor.
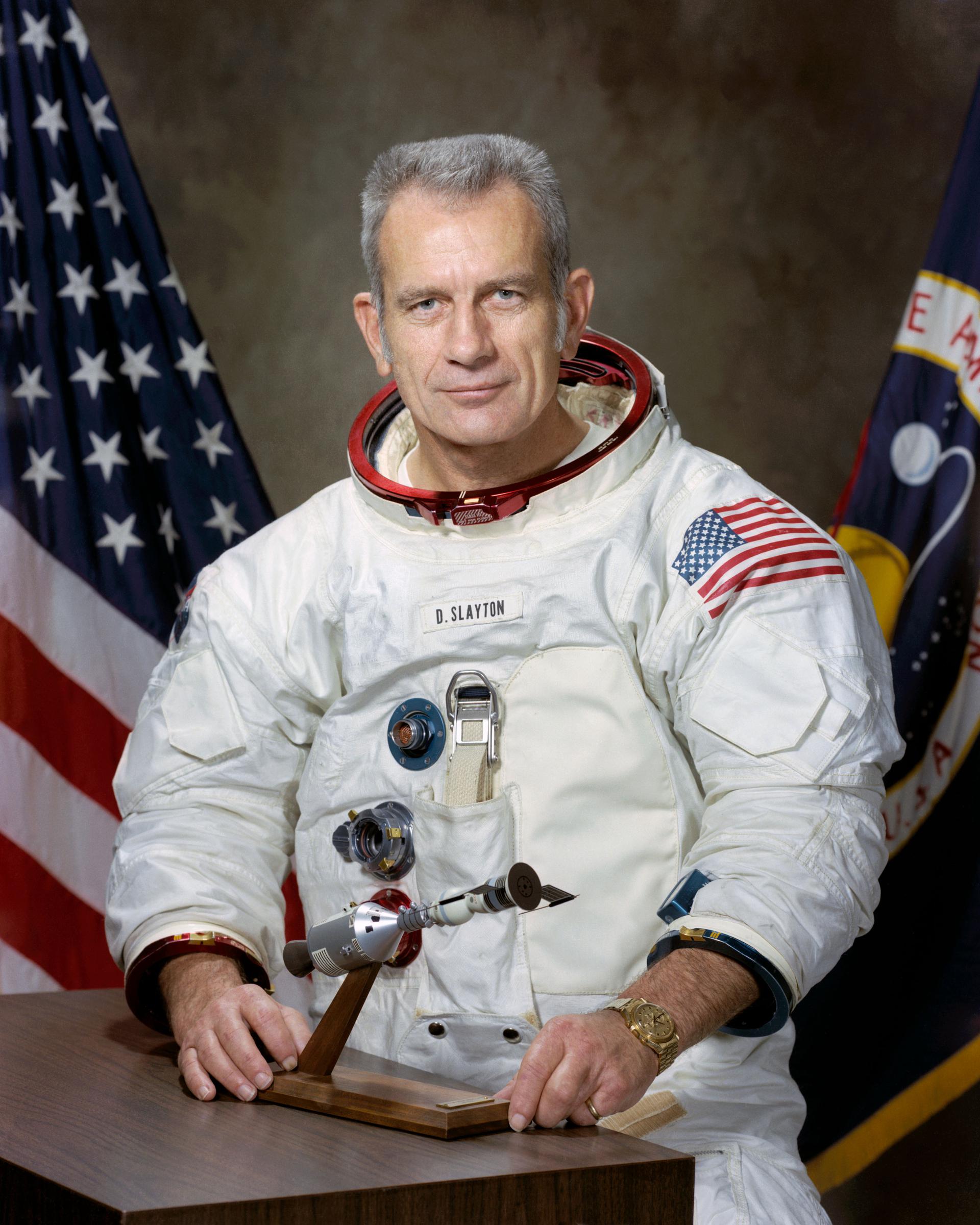

Deke Slayton
- Birthday: 03/01/1924
- Role: Docking Module Pilot
- Nationality: American
- First Flight: 07/15/1975
- Last Flight: 07/15/1975
Donald Kent “Deke” Slayton, was an American World War II pilot, aeronautical engineer, and test pilot who was selected as one of the original NASA Mercury Seven astronauts, and became NASA’s first Chief of the Astronaut Office.
Mission
Apollo-Soyuz Test Project
- Type: Human Exploration
- Orbit: Low Earth Orbit
The Apollo-Soyuz Test Project was the first joint US-Soviet space flight and the last crewed US space mission until the Space Shuttle program.
The US side of mission began on July 15, 1975, 19:50:00 UTC, launching Commander Thomas P. Stafford, Command Module Pilot Vance D. Brand and Docking Module Pilot Donald K. Slayton into orbit. Two days later, they docked with the Soyuz 19 spacecraft. American and Soviet crews visited each other’s spacecrafts, performed docking and redocking maneuvers, conducted joint scientific experiments, exchanged flags and gifts. Crews spent more than 44 hours together, and after final parting of the ships on July 19, Apollo crew spent nine more days in orbit, conducting Earth observation experiments.
The Apollo crew returned to Earth on July 24, 1975, 21:18:0 UTC with a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
Location
Rocket
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Saturn IB
The Saturn IB (pronounced “one B”, also known as the Uprated Saturn I) was an American launch vehicle commissioned by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) for the Apollo program. It replaced the S-IV second stage of the Saturn I with the much more powerful S-IVB, able to launch a partially fueled Apollo Command/Service Module (CSM) or a fully fueled Lunar Module (LM) into low Earth orbit for early flight tests before the larger Saturn V needed for lunar flight was ready.
Agency
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for the civilian space program, as well as aeronautics and aerospace research. NASA have many launch facilities but most are inactive. The most commonly used pad will be LC-39B at Kennedy Space Center in Florida.