Cartosat-3 & others
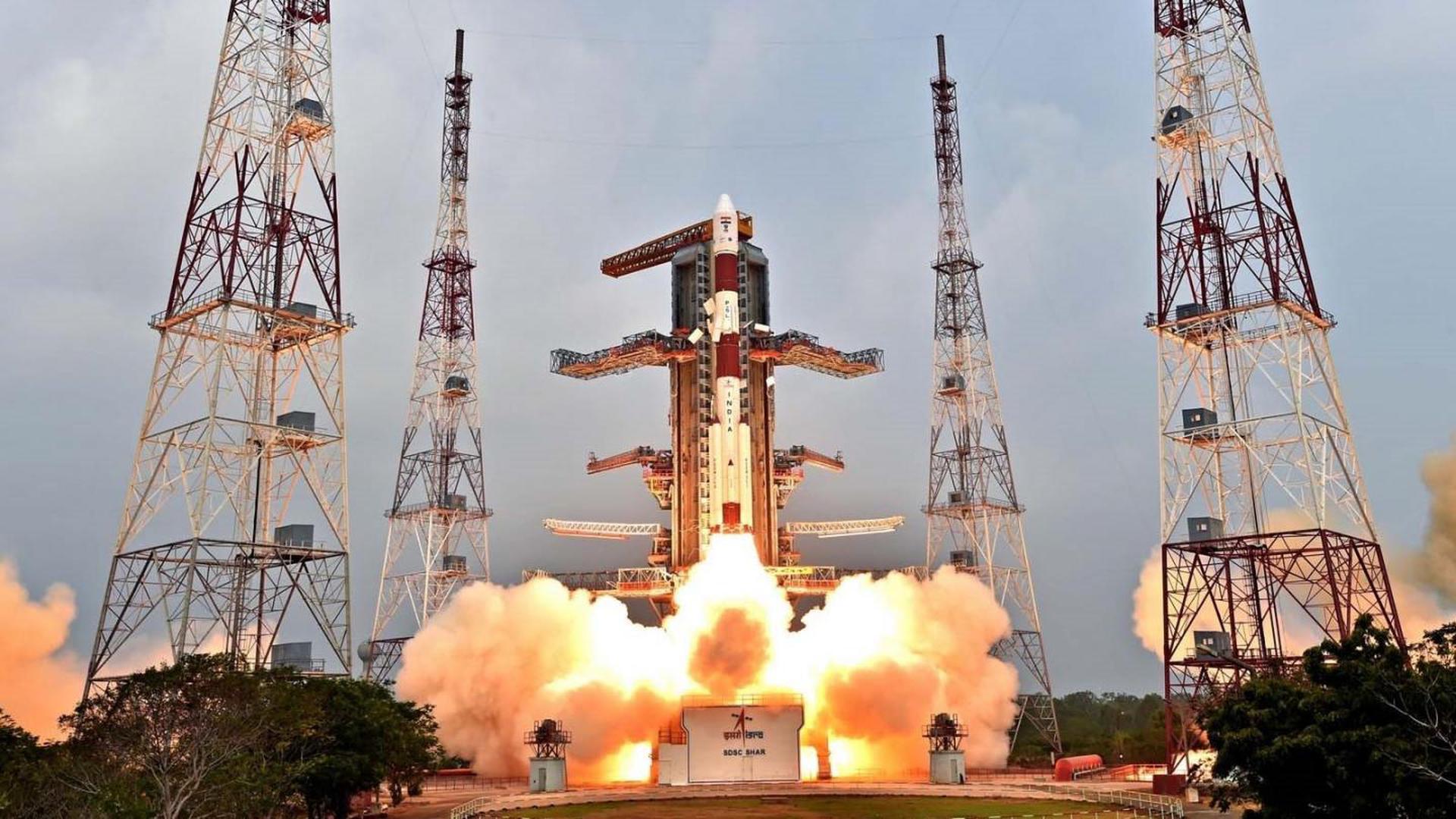
PSLV-XL
Indian Space Research Organization
Mission
Cartosat-3 & others
- Type: Earth Science
- Orbit: Sun-Synchronous Orbit
Cartosat-3 is an advanced remote sensing satellite with high resolution imaging capability developed by ISRO. It’s designed as a follow-on to the Cartosat-2 series. Many new technologies/elements were developed for it like highly agile structural platform, payload platform, higher rate data handling and transmission systems, advanced onboard computer and new power electronics, dual gimbal antenna, etc.
This mission also carries 13 rideshare payloads, including 12 SuperDove cubesats and a technology demonstration Meshbed cubesat.
Location
Satish Dhawan Space Centre Second Launch Pad
Satish Dhawan Space Centre, India
Satish Dhawan Space Centre Second Launch Pad has witnessed the launch of 28 rockets, including 27 orbital launch attempts, while Satish Dhawan Space Centre, India, has been the site for 94 rocket launches.
Rocket
Indian Space Research Organization PSLV XL
PSLV-XL is the upgraded version of Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle in its standard configuration boosted by more powerful, stretched strap-on boosters with 12 tonne propellant load. Weighing 320t at lift-off, the vehicle uses larger strap-on motors (PSOM-XL or S12) to achieve higher payload capability. On 29 December 2005, ISRO successfully tested the improved version of strap-on booster for the PSLV. The first use of PSLV-XL was the launch of Chandrayaan-1 by PSLV C11. The payload capability for this variant is 1,800 kg to SSO.
Agency
Indian Space Research Organization
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is the space agency of the Government of India headquartered in the city of Bangalore. Its vision is to “harness space technology for national development while pursuing space science research and planetary exploration.”