Mars-96
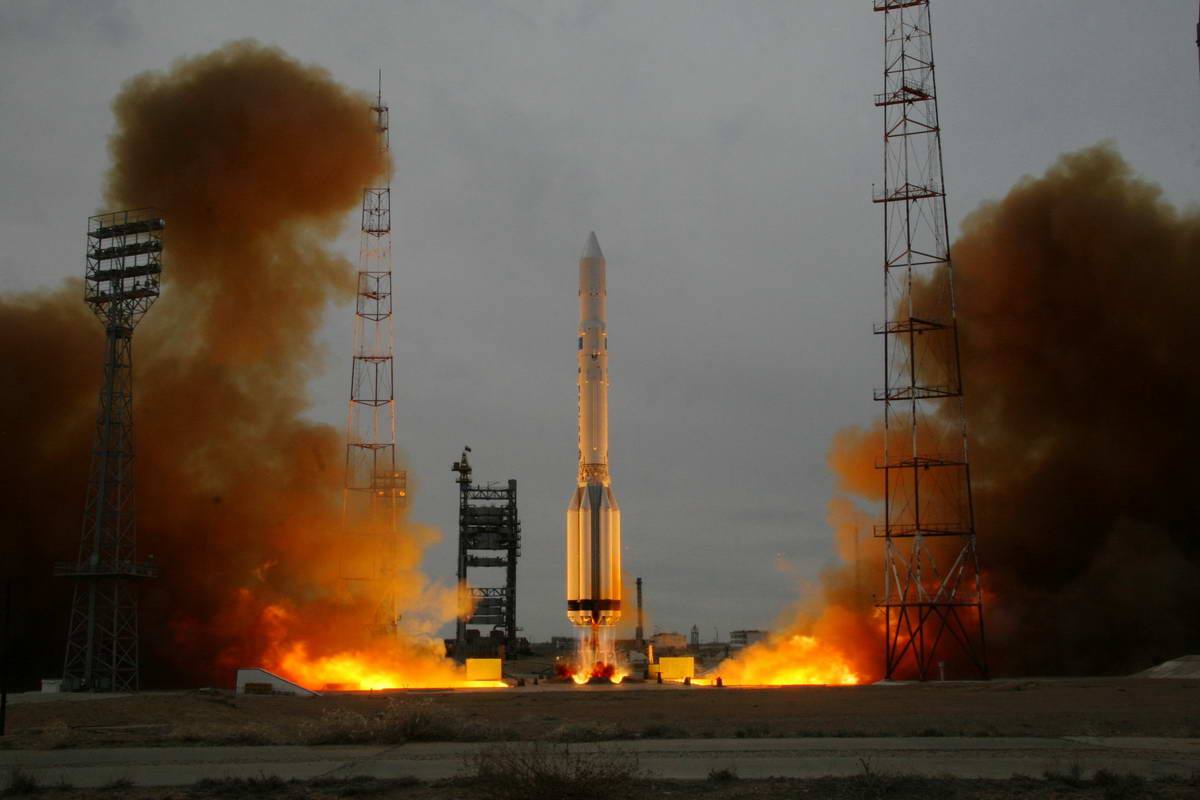
Proton-K/D-2
Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center
Mission
Mars-96
- Type: Robotic Exploration
- Orbit: Heliocentric N/A
The Mars 96 spacecraft was launched into Earth orbit, but failed to achieve insertion into Mars cruise trajectory and re-entered the Earth’s atmosphere at about 00:45 to 01:30 UT on 17 November 1996 and crashed within a presumed 320 km by 80 km area which includes parts of the Pacific Ocean, Chile, and Bolivia. The cause of the crash is not known.
Location
200/39 (200L)
Baikonur Cosmodrome, Republic of Kazakhstan
200/39 (200L) has witnessed the launch of 167 rockets, including 167 orbital launch attempts, while Baikonur Cosmodrome, Republic of Kazakhstan, has been the site for 1547 rocket launches.
Rocket
Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center Proton-K/D-2
The Proton-K was a Russian, previously Soviet, carrier rocket derived from the earlier Proton. It was built by Khrunichev, and launched from sites 81 and 200 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan.
Agency
Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center
Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center is a Moscow-based producer of spacecraft and space-launch systems, including the Proton and Rokot rockets and is currently developing the Angara rocket family. The Proton launch vehicle launches from Baikonur and Rokot launches from Baikonur and Plesetsk. Angara will launch from Plesetsk and Vostochny.