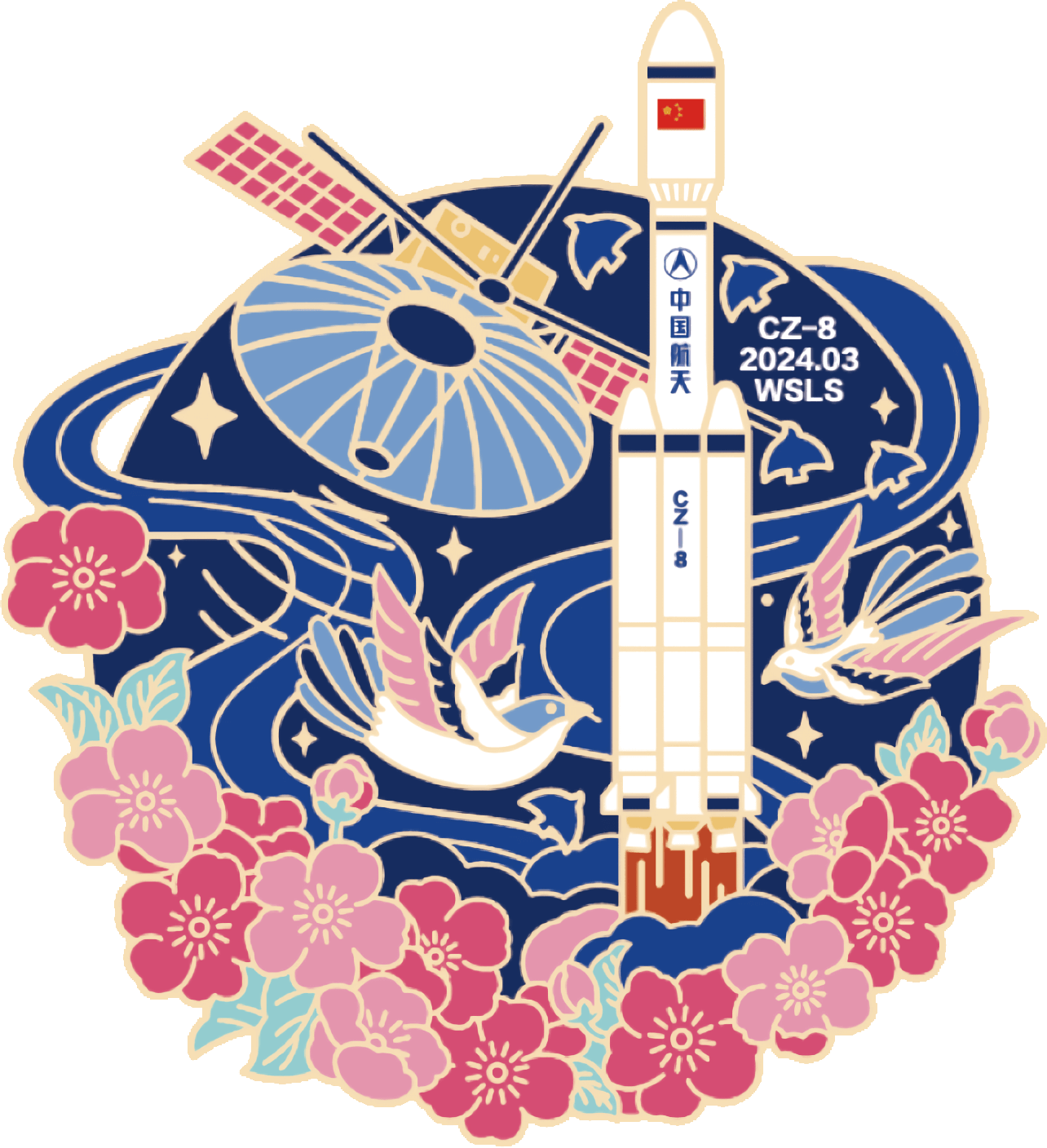
Queqiao-2
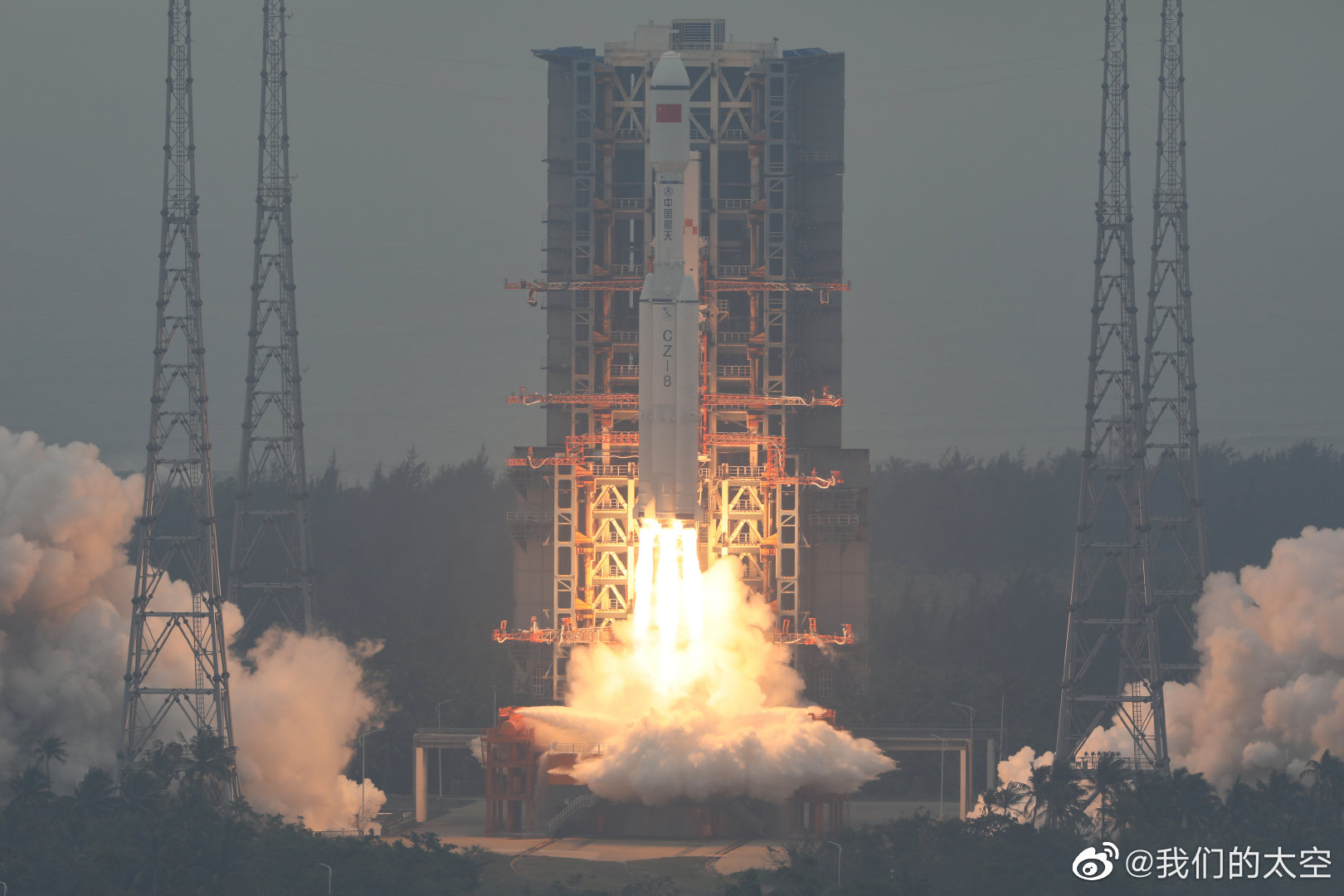
Long March 8
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
Mission
Queqiao-2
- Type: Planetary Science
- Orbit: Lunar Orbit
Queqiao-2 is a Chinese artificial satellite to serve as a communications relay for future Chinese lunar far side missions that cannot communicate directly with the Earth, beginning with the Chang’e 6 lunar sample return mission in 2024.
It will operate from a Distant Retrograde Orbit (DRO) of the Moon.
The launch also carries the Tiandu-1 & 2 small satellites testing cis-lunar space navigation and inter-satellite communication techniques for CNSA’s Deep Space Exploration Laboratory (DSEL).
Location
Rocket
Agency
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
The China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC) is the main contractor for the Chinese space program. It is state-owned and has a number of subordinate entities which design, develop and manufacture a range of spacecraft, launch vehicles, strategic and tactical missile systems, and ground equipment. It was officially established in July 1999 as part of a Chinese government reform drive, having previously been one part of the former China Aerospace Corporation. Various incarnations of the program date back to 1956.