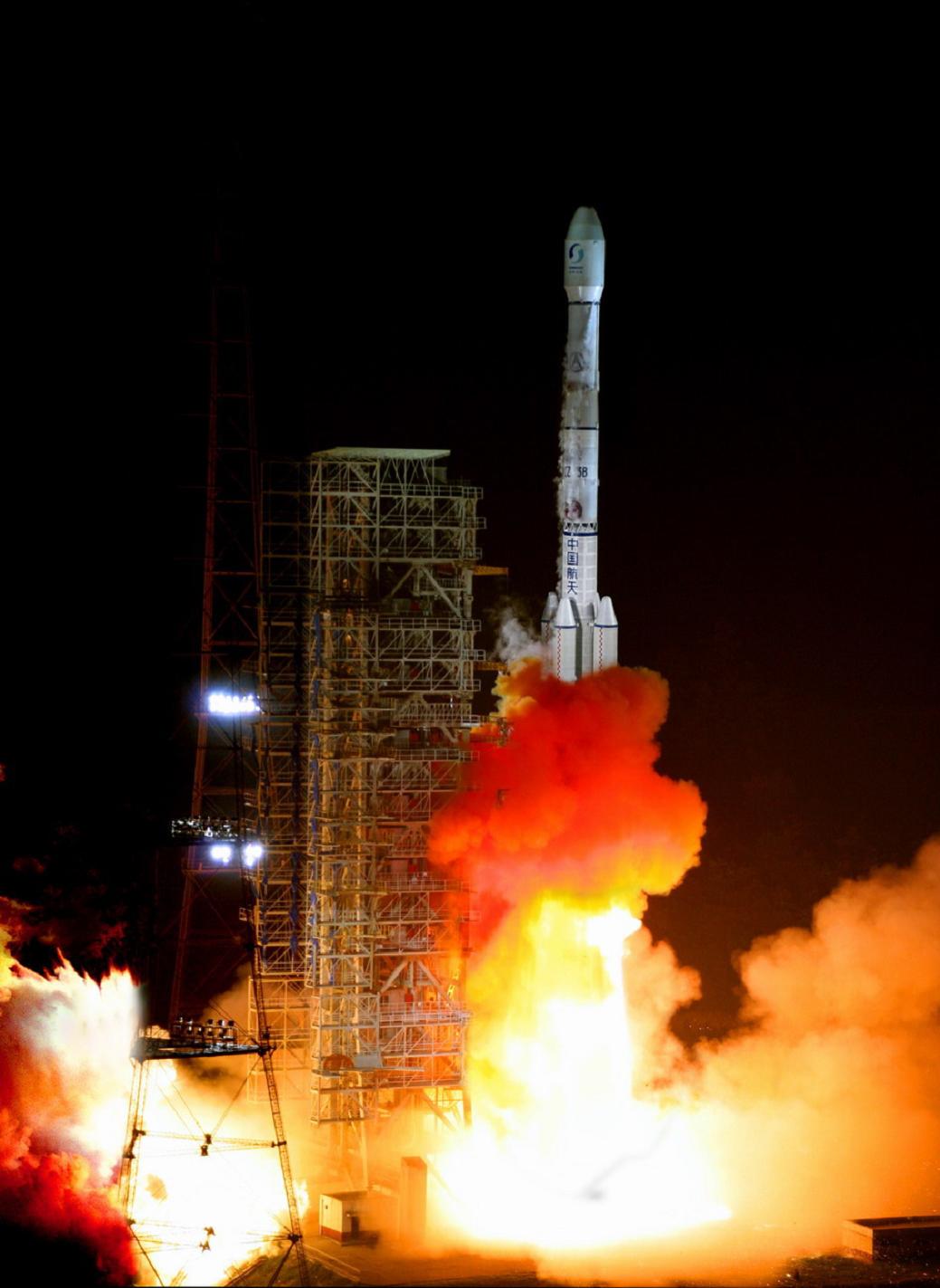
Shijian-13/Chinasat-16
Long March 3B
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
Mission
Shijian-13/Chinasat-16
- Type: Communications
- Orbit: Geostationary Transfer Orbit
- Launch Cost: $70,000,000
This is a Chinese experimental geostationary communications satellite. Besides testing the electric propulsion, the satellite is also reported to carry Chinas first high-throughput satellite payload (HTS), with a capacity of 20 GB per second. The satellite is aiming to provide Ka-band satellite broadband and multimedia services. Additionally it is also to conduct space-to-ground laser communications experiments.
Location
Launch Complex 3 (LC-3/LA-1)
Xichang Satellite Launch Center, People’s Republic of China
Launch Complex 3 (LC-3/LA-1) has witnessed the launch of 89 rockets, including 89 orbital launch attempts, while Xichang Satellite Launch Center, People’s Republic of China, has been the site for 202 rocket launches.
Rocket
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation Long March 3B
The Long March 3B is a Chinese orbital carrier rocket. Introduced in 1996, it is launched from Launch Area 2 and 3 at the Xichang Satellite Launch Center in Sichuan. A three-stage rocket with four strap-on liquid rocket boosters, it is currently the most powerful member of the Long March rocket family and the heaviest of the Long March 3 rocket family, and is mainly used to place communications satellites into geosynchronous orbits.
Agency
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
The China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC) is the main contractor for the Chinese space program. It is state-owned and has a number of subordinate entities which design, develop and manufacture a range of spacecraft, launch vehicles, strategic and tactical missile systems, and ground equipment. It was officially established in July 1999 as part of a Chinese government reform drive, having previously been one part of the former China Aerospace Corporation. Various incarnations of the program date back to 1956.