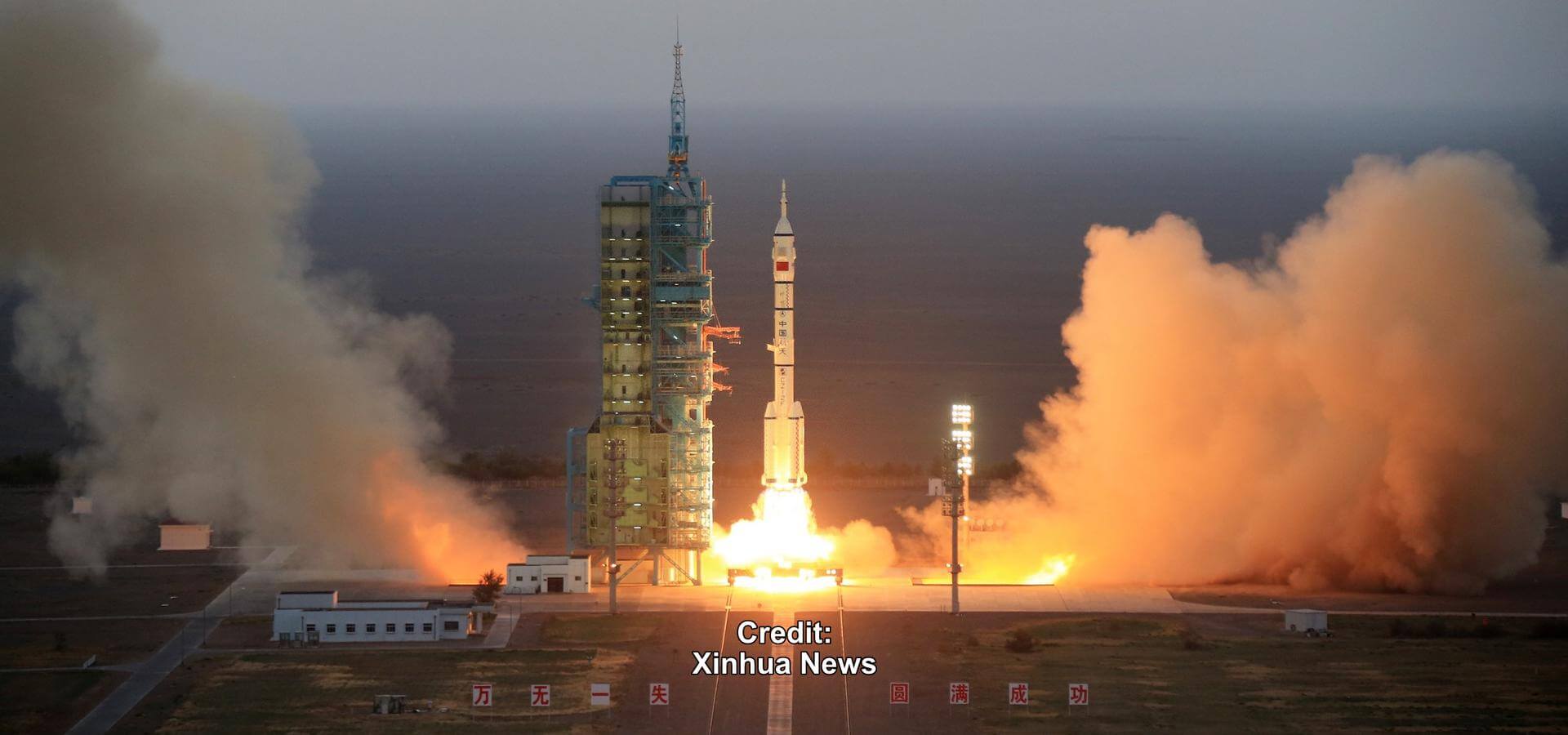
Shenzhou-4
Long March 2F
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
Mission
Shenzhou-4
- Type: Human Exploration
- Orbit: Low Earth Orbit
Fourth and final test flight of the Shenzhou spacecraft, without crew on board. The spacecraft was flown in the same configuration as a crew-carrying mission, and as such two dummy astronauts were carried on board, as are sleeping bags, food and medication. The control systems were fitted with ability for manual control and emergency landing. The windows were constructed of a new material that was designed to stay clear even after reentry to allow an astronaut to confirm that the parachutes have deployed properly.
The spacecraft carried 100 peony seeds to investigate the effect of weightlessness on plants grown from them. The 52 experiments onboard investigated areas in physics, biology, medicine, earth observation, material science, and astronomy.
Location
Launch Area 4 (SLS-1 / 921)
Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, People’s Republic of China
Launch Area 4 (SLS-1 / 921) has witnessed the launch of 22 rockets, including 22 orbital launch attempts, while Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, People’s Republic of China, has been the site for 222 rocket launches.
Rocket
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation Long March 2F
The Long March 2F is a Chinese orbital carrier rocket, part of the Long March 2 rocket family. Designed to launch the crewed Shenzhou spacecraft, the Long March 2F is a human-rated two-stage version of the Long March 2E rocket, which in turn was based on the Long March 2C launch vehicle. It is launched from complex SLS at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center.
Agency
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
The China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC) is the main contractor for the Chinese space program. It is state-owned and has a number of subordinate entities which design, develop and manufacture a range of spacecraft, launch vehicles, strategic and tactical missile systems, and ground equipment. It was officially established in July 1999 as part of a Chinese government reform drive, having previously been one part of the former China Aerospace Corporation. Various incarnations of the program date back to 1956.