Xihe (CHASE)
Long March 2D
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
Mission
Xihe (CHASE)
- Type: Heliophysics
- Orbit: Sun-Synchronous Orbit
- Launch Cost: $30,000,000
Xihe, also known as the Chinese Hα Solar Explorer (CHASE), is designed to test a newly developed satellite platform and conduct solar observations. The scientific payload of the satellite is an Hα imaging spectrograph (HIS), which can, for the first time, acquire full-disk spectroscopic solar observations in the Hα waveband. It will complement the observations by on-orbit solar spacecraft (such as SDO, IRIS, STEREO and PSP), as well as future solar missions of the Solar Orbiter and the Chinese Advanced Space-based Solar Observatory (ASO-S).
Mission is named Xihe after a solar deity from Chinese mythology.
Location
Rocket
Agency
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
The China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC) is the main contractor for the Chinese space program. It is state-owned and has a number of subordinate entities which design, develop and manufacture a range of spacecraft, launch vehicles, strategic and tactical missile systems, and ground equipment. It was officially established in July 1999 as part of a Chinese government reform drive, having previously been one part of the former China Aerospace Corporation. Various incarnations of the program date back to 1956.
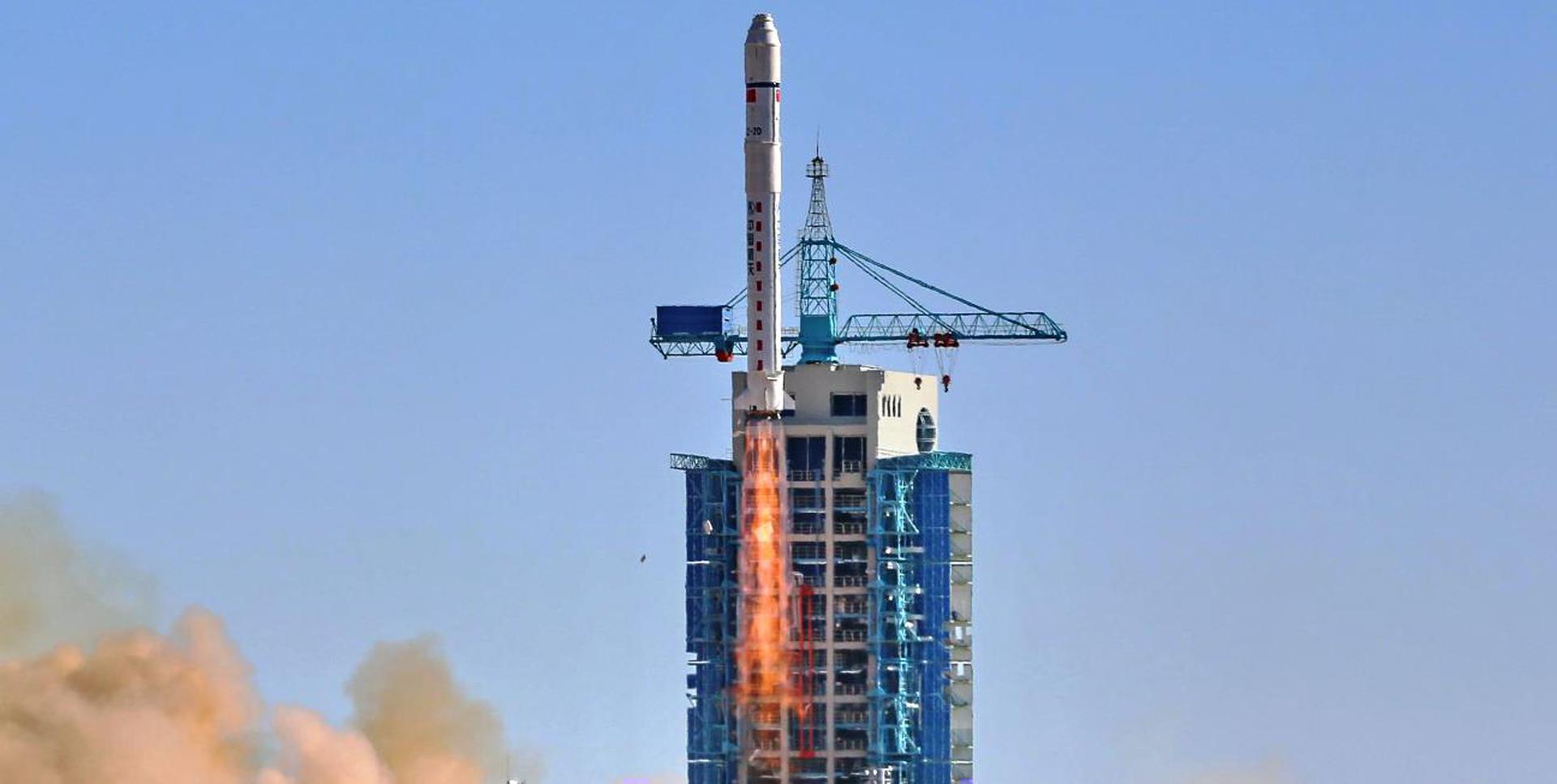



Solar observations, here is to a good launch for all involved.
Great coverage of the launch and program objectives regardless of how short the footage was.
Its always worthy seeing space technology at its best like this, well done to all involved after all “space” is for us all to fully share .