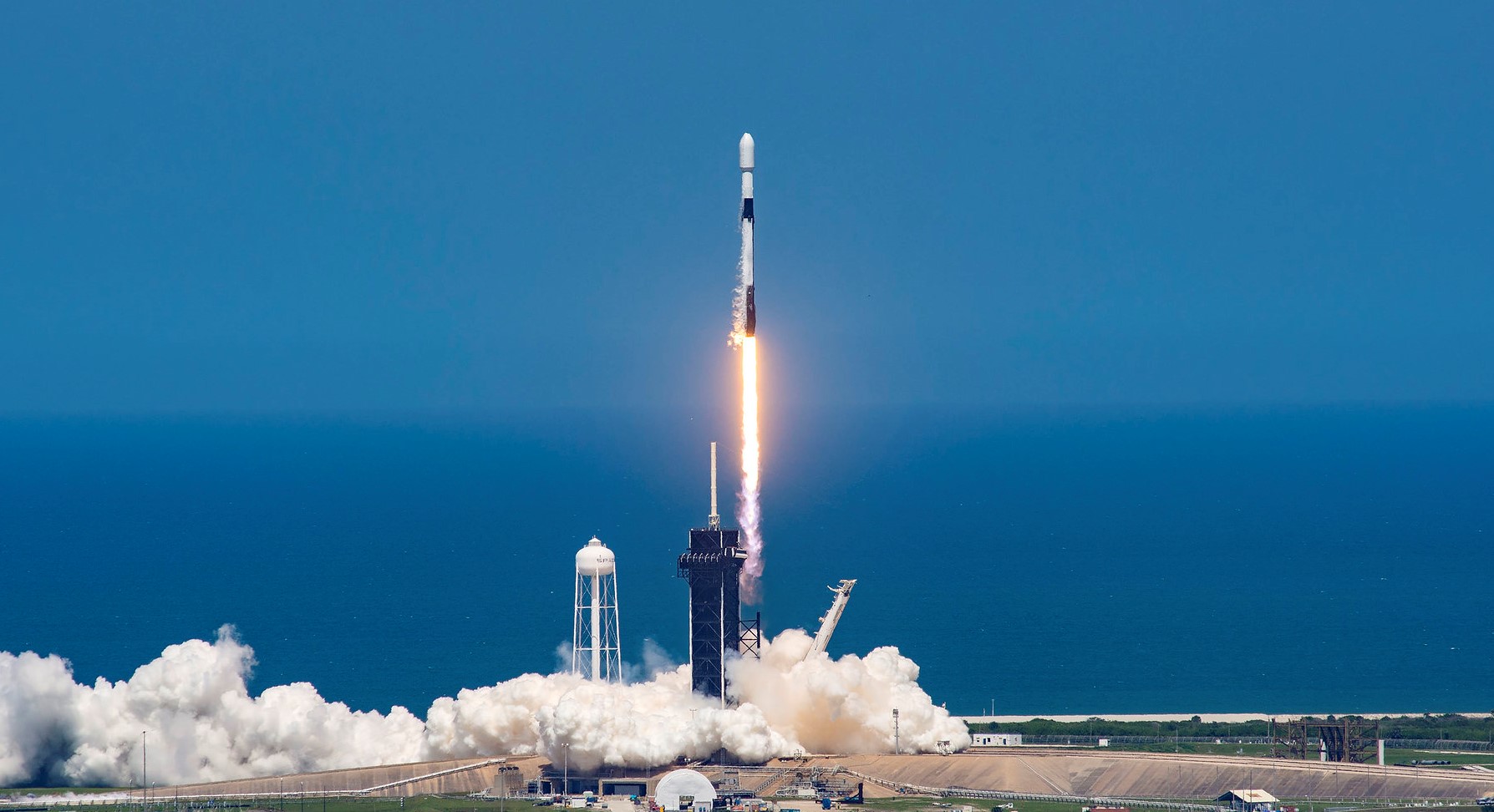
Eutelsat 36D
Falcon 9 Block 5
SpaceX
Weather Forecast During Launch
According to weather officials, there’s a 96% chance of favorable weather conditions at the time of the launch.
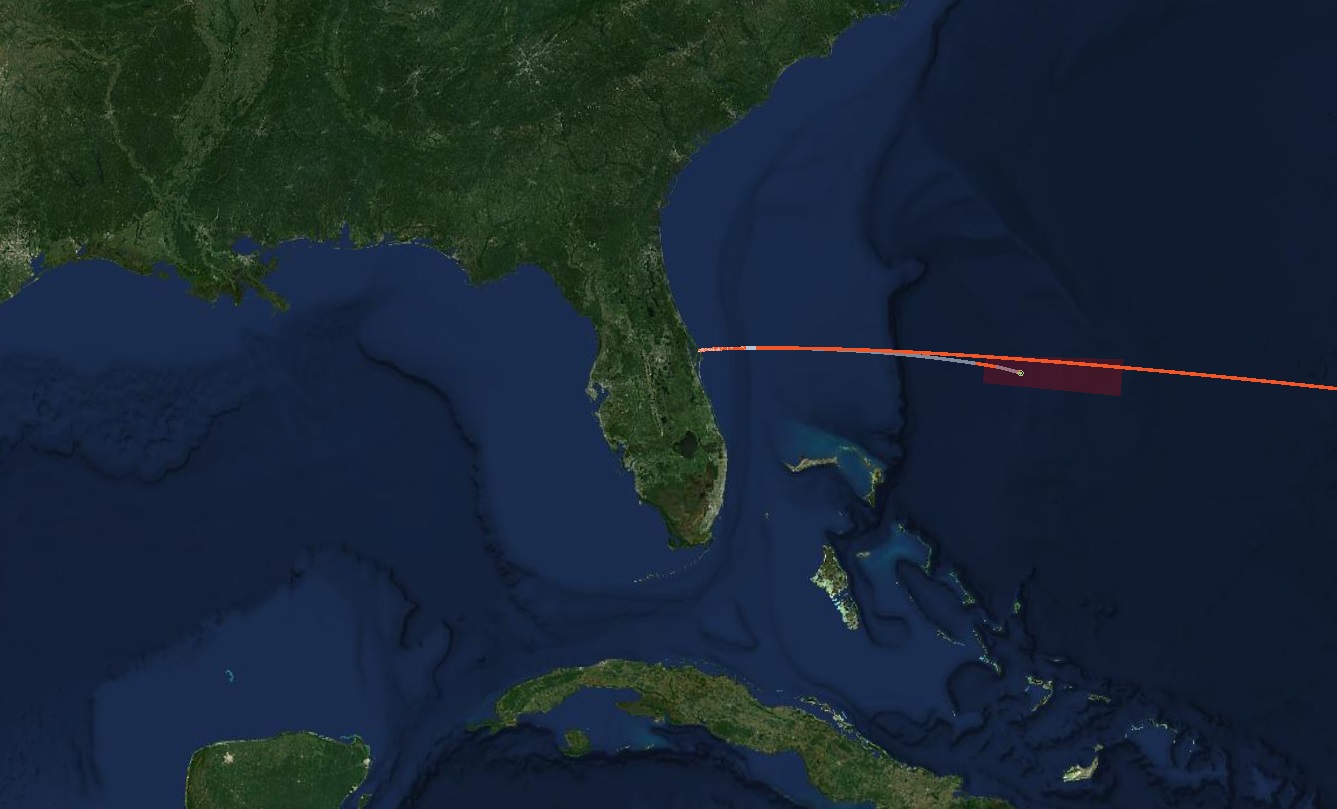
Trajectory
View comprehensive details including the rocket’s trajectory, velocity, altitude, thrust, and more at FlightClub.io.
Mission
Eutelsat 36D
- Type: Communications
- Orbit: Geostationary Transfer Orbit
- Launch Cost: $52,000,000
Eutelsat 36D is a planned new generation multi-mission geostationary telecommunications satellite for Eutelsat, replacing and enhance capacity at 36° East, a key orbital slot for Eutelsat for TV broadcasting (DTH) and government services over Africa, Russia, and Europe.
It is based on the Airbus Eurostar-Neo platform, with electric power generation capability of 18 kW, EOR (Electric Orbit Raising) capability, and a launch mass of 5 tons.
With 70 Ku-band transponders over five downlink beams and a steerable antenna, Eutelsat 36D provides flexibility and performance optimisation to deliver service in Africa, Russia and Europe for an operational lifetime of more than 15 years.
Location
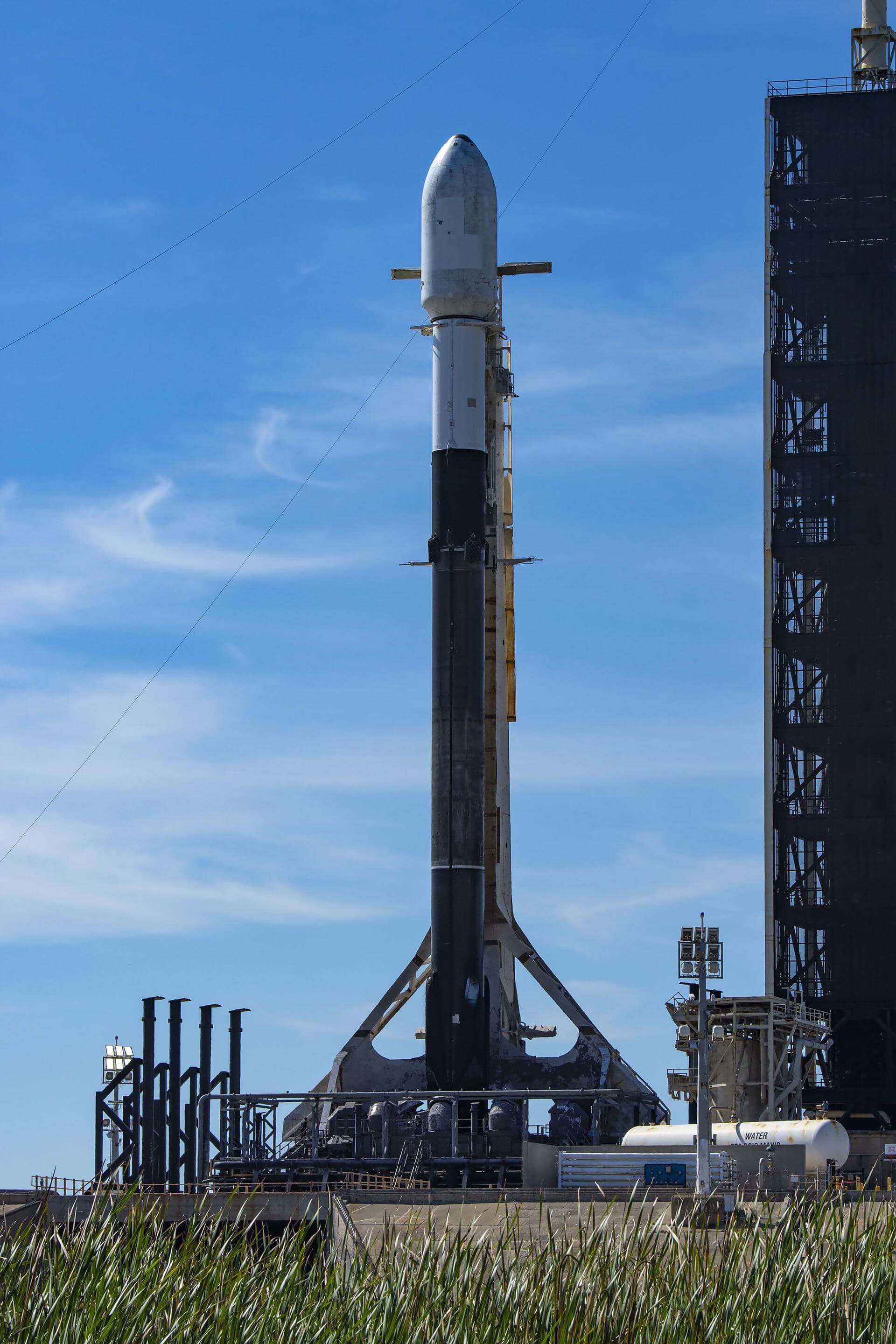
Rocket
Landing
Core B1076
Booster B1076 last launched 03/30/2024 and has seen 12 successful launches and landings. Booster first launched the CRS-26 mission.
Just Read the Instructions – JRTI
Third (Marmac 303) ASDS barge, Just Read the Instructions (JRTI) is currently used to recover Falcon 9 and Heavy boosters in the Altantic Ocean.
Autonomous Spaceport Drone Ship – ASDS
An autonomous spaceport drone ship (ASDS) is an ocean-going vessel derived from a deck barge, outfitted with station-keeping engines and a large landing platform. Construction of such ships was commissioned by aerospace company SpaceX to allow for recovery of rocket first-stages at sea for high-velocity missions which do not carry enough fuel to return to the launch site after lofting spacecraft onto an orbital trajectory.
Agency
SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp., known as SpaceX, is an American aerospace manufacturer and space transport services company headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by entrepreneur Elon Musk with the goal of reducing space transportation costs and enabling the colonization of Mars. SpaceX operates from many pads, on the East Coast of the US they operate from SLC-40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station and historic LC-39A at Kennedy Space Center. They also operate from SLC-4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California, usually for polar launches. Another launch site is being developed at Boca Chica, Texas.